GDNF is a novel ethanol-responsive gene in the VTA: implications for the development and persistence of excessive drinking
- PMID: 23298382
- PMCID: PMC3626755
- DOI: 10.1111/adb.12028
GDNF is a novel ethanol-responsive gene in the VTA: implications for the development and persistence of excessive drinking
Abstract
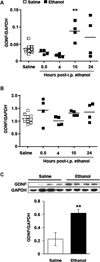
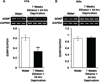
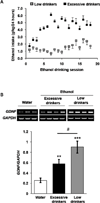
Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) is a potent inhibitor of ethanol consumption and relapse, and GDNF heterozygous knockout mice display increased reward sensitivity to ethanol and consume more ethanol after a period of abstinence than their wild-type littermates. Here, we tested whether ethanol alters GDNF expression in the ventral tegmental area (VTA; GDNF's site of action) and/or the nucleus accumbens (NAc; the main source of GDNF), and if so, determine the role of the endogenous growth factor in the regulation of ethanol consumption. Systemic administration of ethanol increased GDNF expression and protein levels in the VTA, but not the NAc. Additionally, GDNF levels were elevated after an ethanol-drinking session in rats that consumed ethanol in the intermittent-access two-bottle choice procedure for 1 week, but not 7 weeks. Deprivation following 7 weeks of excessive ethanol intake reduced GDNF levels, while a short ethanol binge drinking period following deprivation upregulated GDNF expression. Importantly, knockdown of GDNF within the VTA using adenovirus expressing short hairpin RNA facilitated the escalation of ethanol drinking by ethanol-naïve rats, but not by rats with a history of excessive ethanol consumption. These results suggest that during initial ethanol-drinking experiences, GDNF in the VTA is increased and protects against the development of excessive ethanol intake. However, the growth factor's protective response to ethanol breaks down after protracted excessive ethanol intake and withdrawal, resulting in persistent, excessive ethanol consumption.
Keywords: Addiction; GDNF; VTA; ethanol; growth factor.
© 2013 The Authors, Addiction Biology © 2013 Society for the Study of Addiction.
Figures
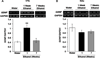

References
-
- Airaksinen M, Saarma M. The GDNF family: signaling, biological functions and therapeutic value. Nature Reviews Neuroscience. 2002;3:383–393. - PubMed
-
- Barroso-Chinea P, Cruz-Muros I, Aymerich MS, Rodriguez-Diaz M, Afonso-Oramas D, Lanciego JL, Gonzalez-Hernandez T. Striatal expression of GDNF and differential vulnerability of midbrain dopaminergic cells. Eur J Neurosci. 2005;21:1815–1827. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

