Reduced levels of chloroplast FtsH protein in tobacco mosaic virus-infected tobacco leaves accelerate the hypersensitive reaction
- PMID: 10852937
- PMCID: PMC149093
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.12.6.917
Reduced levels of chloroplast FtsH protein in tobacco mosaic virus-infected tobacco leaves accelerate the hypersensitive reaction
Abstract
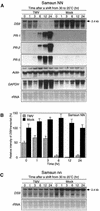
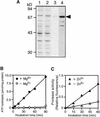
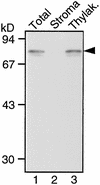
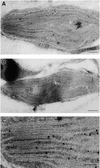
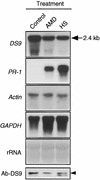
In tobacco cultivars resistant to tobacco mosaic virus (TMV), infection results in the death of the infected cells accompanying the formation of necrotic lesions. To identify the genes involved in this hypersensitive reaction, we isolated the cDNA of tobacco DS9, the transcript of which decreases before the appearance of necrotic lesions. The DS9 gene encodes a chloroplastic homolog of bacterial FtsH protein, which serves to maintain quality control of some cytoplasmic and membrane proteins. A large quantity of DS9 protein was found in healthy leaves, whereas the quantity of DS9 protein in infected leaves decreased before the lesions appeared. In transgenic tobacco plants containing less and more DS9 protein than wild-type plants, the necrotic lesions induced by TMV were smaller and larger, respectively, than those on wild-type plants. These results suggest that a decrease in the level of DS9 protein in TMV-infected cells, resulting in a subsequent loss of function of the chloroplasts, accelerates the hypersensitive reaction.
Figures



References
-
- Adam, Z. (1996). Protein stability and degradation in chloroplasts. Plant Mol. Biol. 32, 773–783. - PubMed
-
- Akiyama, Y., Shirai, Y., and Ito, K. (1994). Involvement of FtsH in protein assembly into and through the membrane. II. Dominant mutations affecting FtsH functions. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 5225–5229. - PubMed
-
- Akiyama, Y., Kihara, A., and Ito, K. (1996. a). Subunit a of proton ATPase F0 sector is a substrate of the FtsH protease in Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 399, 26–28. - PubMed
-
- Akiyama, Y., Kihara, A., Tokuda, H., and Ito, K. (1996. b). FtsH (HflB) is an ATP-dependent protease selectively acting on SecY and some other membrane proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 31196–31201. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

