Widespread A-to-I RNA editing of Alu-containing mRNAs in the human transcriptome
- PMID: 15534692
- PMCID: PMC526178
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0020391
Widespread A-to-I RNA editing of Alu-containing mRNAs in the human transcriptome
Abstract
RNA editing by adenosine deamination generates RNA and protein diversity through the posttranscriptional modification of single nucleotides in RNA sequences. Few mammalian A-to-I edited genes have been identified despite evidence that many more should exist. Here we identify intramolecular pairs of Alu elements as a major target for editing in the human transcriptome. An experimental demonstration in 43 genes was extended by a broader computational analysis of more than 100,000 human mRNAs. We find that 1,445 human mRNAs (1.4%) are subject to RNA editing at more than 14,500 sites, and our data further suggest that the vast majority of pre-mRNAs (greater than 85%) are targeted in introns by the editing machinery. The editing levels of Alu-containing mRNAs correlate with distance and homology between inverted repeats and vary in different tissues. Alu-mediated RNA duplexes targeted by RNA editing are formed intramolecularly, whereas editing due to intermolecular base-pairing appears to be negligible. We present evidence that these editing events can lead to the posttranscriptional creation or elimination of splice signals affecting alternatively spliced Alu-derived exons. The analysis suggests that modification of repetitive elements is a predominant activity for RNA editing with significant implications for cellular gene expression.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no conflicts of interest exist.
Figures


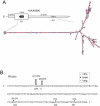
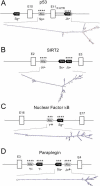
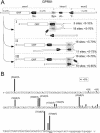
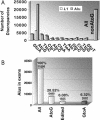
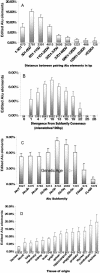
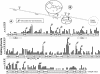
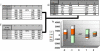
References
-
- Ausubel FM, Brent R, Kingston RE, Moore DD, Seidman JG, et al. Current protocols in molecular biology (vols. 1–4) New York: Wiley; 1995.
-
- Baltimore D. Our genome unveiled. Nature. 2001;409:814–816. - PubMed
-
- Bass BL, Weintraub H. A developmentally regulated activity that unwinds RNA duplexes. Cell. 1987;48:607–613. - PubMed
-
- Batzer MA, Deininger PL. Alu repeats and human genomic diversity. Nat Rev Genet. 2002;3:370–379. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

