Molecular cloning of a Babesia caballi gene encoding the 134-kilodalton protein and evaluation of its diagnostic potential in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
- PMID: 14715570
- PMCID: PMC321337
- DOI: 10.1128/cdli.11.1.211-215.2004
Molecular cloning of a Babesia caballi gene encoding the 134-kilodalton protein and evaluation of its diagnostic potential in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
Abstract
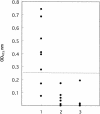
A Babesia caballi gene encoding the 134-kDa (BC134) protein was immunoscreened with B. caballi-infected horse serum. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) using recombinant BC134 protein could effectively differentiate B. caballi-infected horse sera from Babesia equi-infected or noninfected control horse sera. These results suggest that the recombinant BC134 protein is a potential diagnostic antigen in the detection of B. caballi infection.
Figures




References
-
- Bashiruddin, J. D., C. Camma, and E. Revelo. 1999. Molecular detection of Babesia equi and Babesia caballi in horse blood by PCR amplification of part of the 16S rRNA gene. Vet. Parasitol. 84:75-83. - PubMed
-
- Böse, R., and B. Peymann. 1994. Diagnosis of Babesia caballi infections in horses by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and Western blot. Int. J. Parasitol. 24:341-346. - PubMed
-
- Brüning, A., P. Phipps, E. Posnett, and E. U. Canning. 1997. Monoclonal antibodies against Babesia caballi and Babesia equi and their application in serodiagnosis. Vet. Parasitol. 58:11-26. - PubMed
-
- Friedhoff, K. T. 1982. The piroplasms of equidae. Significance for the international equine trade. Berl. Muench. Tieraerztl. Wochenschr. 95:368-374. - PubMed
-
- Friedhoff, K. T., A. M. Tenter, and I. Müller. 1990. Haemoparasites of equines: impact on the international trade of horses. Rev. Sci. Technol. 9:1187-1194. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

