Complete nucleotide sequence of TOL plasmid pDK1 provides evidence for evolutionary history of IncP-7 catabolic plasmids
- PMID: 20581207
- PMCID: PMC2937381
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00359-10
Complete nucleotide sequence of TOL plasmid pDK1 provides evidence for evolutionary history of IncP-7 catabolic plasmids
Erratum in
- J Bacteriol. 2010 Oct;192(20):5558
Abstract
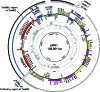
To understand the mechanisms for structural diversification of Pseudomonas-derived toluene-catabolic (TOL) plasmids, the complete sequence of a self-transmissible plasmid pDK1 with a size of 128,921 bp from Pseudomonas putida HS1 was determined. Comparative analysis revealed that (i) pDK1 consisted of a 75.6-kb IncP-7 plasmid backbone and 53.2-kb accessory gene segments that were bounded by transposon-associated regions, (ii) the genes for conjugative transfer of pDK1 were highly similar to those of MOB(H) group of mobilizable plasmids, and (iii) the toluene-catabolic (xyl) gene clusters of pDK1 were derived through homologous recombination, transposition, and site-specific recombination from the xyl gene clusters homologous to another TOL plasmid, pWW53. The minireplicons of pDK1 and its related IncP-7 plasmids, pWW53 and pCAR1, that contain replication and partition genes were maintained in all of six Pseudomonas strains tested, but not in alpha- or betaproteobacterial strains. The recipient host range of conjugative transfer of pDK1 was, however, limited to two Pseudomonas strains. These results indicate that IncP-7 plasmids are essentially narrow-host-range and self-transmissible plasmids that encode MOB(H) group-related transfer functions and that the host range of IncP-7-specified conjugative transfer was, unlike the situation in other well-known plasmids, narrower than that of its replication.
Figures

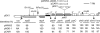


References
-
- Assinder, S. J., P. De Marco, D. J. Osborne, C. L. Poh, L. E. Shaw, M. K. Winson, and P. A. Williams. 1993. A comparison of the multiple alleles of xylS carried by TOL plasmids pWW53 and pDK1 and its implications for their evolutionary relationship. J. Gen. Microbiol. 139:557-568. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

