Lysine decarboxylase catalyzes the first step of quinolizidine alkaloid biosynthesis and coevolved with alkaloid production in leguminosae
- PMID: 22415272
- PMCID: PMC3336119
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.112.095885
Lysine decarboxylase catalyzes the first step of quinolizidine alkaloid biosynthesis and coevolved with alkaloid production in leguminosae
Abstract
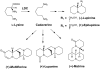
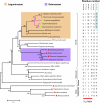
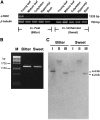
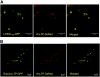
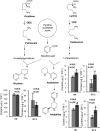
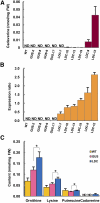
Lysine decarboxylase (LDC) catalyzes the first-step in the biosynthetic pathway of quinolizidine alkaloids (QAs), which form a distinct, large family of plant alkaloids. A cDNA of lysine/ornithine decarboxylase (L/ODC) was isolated by differential transcript screening in QA-producing and nonproducing cultivars of Lupinus angustifolius. We also obtained L/ODC cDNAs from four other QA-producing plants, Sophora flavescens, Echinosophora koreensis, Thermopsis chinensis, and Baptisia australis. These L/ODCs form a phylogenetically distinct subclade in the family of plant ornithine decarboxylases. Recombinant L/ODCs from QA-producing plants preferentially or equally catalyzed the decarboxylation of L-lysine and L-ornithine. L. angustifolius L/ODC (La-L/ODC) was found to be localized in chloroplasts, as suggested by the transient expression of a fusion protein of La-L/ODC fused to the N terminus of green fluorescent protein in Arabidopsis thaliana. Transgenic tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) suspension cells and hairy roots produced enhanced levels of cadaverine-derived alkaloids, and transgenic Arabidopsis plants expressing (La-L/ODC) produced enhanced levels of cadaverine, indicating the involvement of this enzyme in lysine decarboxylation to form cadaverine. Site-directed mutagenesis and protein modeling studies revealed a structural basis for preferential LDC activity, suggesting an evolutionary implication of L/ODC in the QA-producing plants.
Figures

References
-
- Andreadakis A., Kotzabasis K. (1996). Changes in the biosynthesis and catabolism of polyamines in isolated plastids during chloroplast photodevelopment. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 33: 163–170
-
- Arnold K., Bordoli L., Kopp J., Schwede T. (2006). The SWISS-MODEL workspace: A web-based environment for protein structure homology modelling. Bioinformatics 22: 195–201 - PubMed
-
- Bagni N., Tassoni A. (2001). Biosynthesis, oxidation and conjugation of aliphatic polyamines in higher plants. Amino Acids 20: 301–317 - PubMed
-
- Bassez T., Paris J., Omilli F., Dorel C., Osborne H.B. (1990). Post-transcriptional regulation of ornithine decarboxylase in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Development 110: 955–962 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

