Family-based analysis using a dense single-nucleotide polymorphism-based map defines genetic variation at PSORS1, the major psoriasis-susceptibility locus
- PMID: 12148091
- PMCID: PMC379192
- DOI: 10.1086/342289
Family-based analysis using a dense single-nucleotide polymorphism-based map defines genetic variation at PSORS1, the major psoriasis-susceptibility locus
Abstract
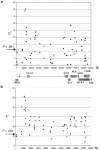
Psoriasis is a common skin disorder of multifactorial origin. Genomewide scans for disease susceptibility have repeatedly demonstrated the existence of a major locus, PSORS1 (psoriasis susceptibility 1), contained within the major histocompatibility complex (MHC), on chromosome 6p21. Subsequent refinement studies have highlighted linkage disequilibrium (LD) with psoriasis, along a 150-kb segment that includes at least three candidate genes (encoding human leukocyte antigen-C [HLA-C], alpha-helix-coiled-coil-rod homologue, and corneodesmosin), each of which has been shown to harbor disease-associated alleles. However, the boundaries of the minimal PSORS1 region remain poorly defined. Moreover, interpretations of allelic association with psoriasis are compounded by limited insight of LD conservation within MHC class I interval. To address these issues, we have pursued a high-resolution genetic characterization of the PSORS1 locus. We resequenced genomic segments along a 220-kb region at chromosome 6p21 and identified a total of 119 high-frequency SNPs. Using 59 SNPs (18 coding and 41 noncoding SNPs) whose position was representative of the overall marker distribution, we genotyped a data set of 171 independently ascertained parent-affected offspring trios. Family-based association analysis of this cohort highlighted two SNPs (n.7 and n.9) respectively lying 7 and 4 kb proximal to HLA-C. These markers generated highly significant evidence of disease association (P<10-9), several orders of magnitude greater than the observed significance displayed by any other SNP that has previously been associated with disease susceptibility. This observation was replicated in a Gujarati Indian case/control data set. Haplotype-based analysis detected overtransmission of a cluster of chromosomes, which probably originated by ancestral mutation of a common disease-bearing haplotype. The only markers exclusive to the overtransmitted chromosomes are SNPs n.7 and n.9, which define a 10-kb PSORS1 core risk haplotype. These data demonstrate the power of SNP haplotype-based association analyses and provide high-resolution dissection of genetic variation across the PSORS1 interval, the major susceptibility locus for psoriasis.
Figures

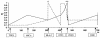
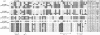
References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- GenBank, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Genbank/ (for the MHC sequence [accession numbers AC004204, AC006048, AC004185, AC006047, AC004195, and AC006163])
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/ (for psoriasis [MIM *177900], HLA-C [MIM *142840], OTF3 [MIM *164177], HCR [MIM *605310], and CDSN [MIM *602593])
References
-
- Allen MH, Veal C, Faassen A, Powis SH, Vaughan RW, Trembath RC, Barker JNWN (1999) A non-HLA gene within the MHC in psoriasis. Lancet 353:1589–1590 - PubMed
-
- Asahina A, Kuwata S, Tokunaga K, Juji T, Nakagawa H (1996) Study of aspartate at residue 9 of HLA-C molecules in Japanese patients with psoriasis vulgaris. J Dermatol Sci 13:125–133 - PubMed
-
- Asumalahti K, Latinen T, Itkonen-Vatjus R Lokki ML, Suomela S, Snellman E, Saarialho-Kere U, Kere J (2000) A candidate gene for psoriasis near HLA-C, HCR (Pg8), is highly polymorphic with a disease-associated susceptibility allele. Hum Mol Genet 9:1533–1542 - PubMed
-
- Asumalahti K, Veal C, Latinen T, Suomela S, Allen M, Outi E, Moser M, et al (2002) Coding haplotype analysis supports HCR as the putative susceptibility gene at the MHC PSORS1 locus. Hum Mol Genet 11:589–597 - PubMed
-
- Balendran N, Clough RL, Arguello JR, Barber R, Veal C, Jones AB, Rosbotham JL, Little AM, Madrigal A, Barker JNWN, Powis SH, Tremabth RC (1999) Characterization of the major susceptibility region for psoriasis at chromosome 6p21.3. J Invest Dermatol 113:322–328 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

