The human Arp2/3 complex is composed of evolutionarily conserved subunits and is localized to cellular regions of dynamic actin filament assembly
- PMID: 9230079
- PMCID: PMC2138188
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.138.2.375
The human Arp2/3 complex is composed of evolutionarily conserved subunits and is localized to cellular regions of dynamic actin filament assembly
Abstract
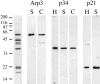
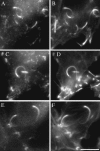
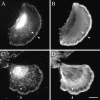
The Arp2/3 protein complex has been implicated in the control of actin polymerization in cells. The human complex consists of seven subunits which include the actin related proteins Arp2 and Arp3, and five others referred to as p41-Arc, p34-Arc, p21-Arc, p20-Arc, and p16-Arc (p omplex). We have determined the predicted amino acid sequence of all seven subunits. Each has homologues in diverse eukaryotes, implying that the structure and function of the complex has been conserved through evolution. Human Arp2 and Arp3 are very similar to family members from other species. p41-Arc is a new member of the Sop2 family of WD (tryptophan and aspartate) repeat-containing proteins and may be posttranslationally modified, suggesting that it may be involved in regulating the activity and/or localization of the complex. p34-Arc, p21-Arc, p20-Arc, and p16-Arc define novel protein families. We sought to evaluate the function of the Arp2/3 complex in cells by determining its intracellular distribution. Arp3, p34-Arc, and p21-Arc were localized to the lamellipodia of stationary and locomoting fibroblasts, as well to Listeria monocytogenes assembled actin tails. They were not detected in cellular bundles of actin filaments. Taken together with the ability of the Arp2/3 complex to induce actin polymerization, these observations suggest that the complex promotes actin assembly in lamellipodia and may participate in lamellipodial protrusion.
Figures




References
-
- Cossart P. Actin-based bacterial motility. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1995;7:94–101. - PubMed
-
- Couch FJ, Rommens JM, Neuhausen SL, Belanger C, Dumont M, Abel K, Bell R, Berry S, Bogden R, Cannon-Albright L, et al. Generation of an integrated transcription map of the BRCA2 region on chromosome 13q12-q13. Genomics. 1996;36:86–99. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

