Cospeciation of chemoautotrophic bacteria and deep sea clams
- PMID: 9707583
- PMCID: PMC21444
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.17.9962
Cospeciation of chemoautotrophic bacteria and deep sea clams
Abstract
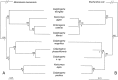
Vesicomyid clams depend entirely on sulfur-oxidizing endosymbiotic bacteria for their nutriment. Endosymbionts that are transmitted cytoplasmically through eggs, such as these, should exhibit a phylogenetic pattern that closely parallels the phylogeny of host mitochondrial genes. Such parallel patterns are rarely observed, however, because they are obscured easily by small amounts of horizontal symbiont transmission or occasional host switching. The present symbiont genealogy, based on bacterial small subunit (16S) rDNA sequences, was closely congruent with the host genealogy, based on clam mitochondrial cytochrome oxidase subunit I and large subunit (16S) rDNA sequences. This phylogenetic evidence supports the hypothesis of cospeciation and a long term association between the participants in this symbiosis.
Figures
References
-
- Lonsdale P. Deep Sea Res. 1977;24:857–863.
-
- Ballard R D. Oceanus. 1977;20:35–44.
-
- Jannasch H W, Wirsen C O. Bioscience. 1979;29:592–602.
-
- Futuyma D J, Slatkin M. Coevolution. Sunderland, MA: Sinauer; 1983. p. 555.
-
- Moran N A, Munson M A, Baumann P, Ishikawa H. Proc R Soc Lond B. 1993;253:167–171.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

