Imprinting of human GRB10 and its mutations in two patients with Russell-Silver syndrome
- PMID: 10856193
- PMCID: PMC1287191
- DOI: 10.1086/302997
Imprinting of human GRB10 and its mutations in two patients with Russell-Silver syndrome
Abstract
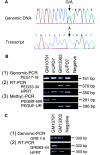
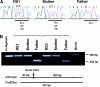
Documentation of maternal uniparental disomy of chromosome 7 in 10% of patients with Russell-Silver syndrome (RSS), characterized by prenatal and postnatal growth retardation and dysmorphic features, has suggested the presence of an imprinted gene on chromosome 7 whose mutation is responsible for the RSS phenotype. Human GRB10 on chromosome 7, a homologue of the mouse imprinted gene Grb10, is a candidate, because GRB10 has a suppressive effect on growth, through its interaction with either the IGF-I receptor or the GH receptor, and two patients with RSS were shown to have a maternally derived duplication of 7p11-p13, encompassing GRB10. In the present study, we first demonstrated that the GRB10 gene is also monoallelically expressed in human fetal brain tissues and is transcribed from the maternally derived allele in somatic-cell hybrids. Hence, human GRB10 is imprinted. A mutation analysis of GRB10 in 58 unrelated patients with RSS identified, within the N-terminal domain of the protein, a P95S substitution in two patients with RSS. In these two cases, the mutant allele was inherited from the mother. The fact that monoallelic GRB10 expression was observed from the maternal allele in this study suggests but does not prove that these maternally transmitted mutant alleles contribute to the RSS phenotype.
Figures
Comment in
-
Conflicting reports of imprinting status of human GRB10 in developing brain: how reliable are somatic cell hybrids for predicting allelic origin of expression?Am J Hum Genet. 2001 Feb;68(2):543-5. doi: 10.1086/318192. Am J Hum Genet. 2001. PMID: 11170901 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- Coriell Cell Repository, http://locus.umdnj.edu/nigms
-
- European Collection of Cell Cultures, http://fuseiv.star.co.uk/camr/
-
- GenBank, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/GenBank/ (for sequences of cDNA [accession number AF001534] and genomic DNA [accession numbers AF073363–AF073378] of human GRB10)
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim (for RSS [MIM 180860])
References
-
- Al-Fifi S, Teebi AS, Shevell M (1996) Autosomal dominant Russell-Silver syndrome. Am J Med Genet 61:96–97 - PubMed
-
- Angrist M, Bolk S, Bentley K, Nallasamy S, Halushka MK, Chakravarti A (1998) Genomic structure of the gene for the SH2 and pleckstrin homology domain-containing protein GRB10 and evaluation of its role in Hirschsprung disease. Oncogene 17:3065–3070 - PubMed
-
- Bernard LE, Penaherrera MS, Van Allen MI, Wang MS, Yong SL, Gareis F, Langlois S, et al (1999) Clinical and molecular findings in two patients with Russell-Silver syndrome and UPD7: comparison with non-UPD7 cases. Am J Med Genet 87:230–236 - PubMed
-
- Cattanach BM, Shibata H, Hayashizaki Y, Townsend KM, Ball S, Beechey CV (1998) Association of a redefined proximal mouse chromosome 11 imprinting region and U2afbp-rs/U2af1-rs1 expression. Cytogenet Cell Genet 80:41–47 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

