Molecular characterization and chromosomal localization of a third alpha-class hypoxia inducible factor subunit, HIF3alpha
- PMID: 9840812
- PMCID: PMC6151950
Molecular characterization and chromosomal localization of a third alpha-class hypoxia inducible factor subunit, HIF3alpha
Abstract
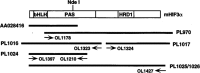
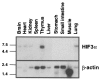
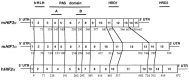
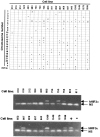
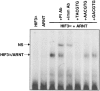
Hypoxia inducible factors (HIFs) are heterodimeric transcription factors that regulate a number of adaptive responses to low oxygen tension. They are composed of alpha- and beta-subunits that belong to the basic helix-loop-helix-PAS (bHLH-PAS) superfamily. In our efforts to identify new bHLH-PAS proteins, we cloned a cDNA encoding a novel alpha-class hypoxia inducible factor, HIF3alpha. The HIF3alpha open reading frame encodes a 662-amino acid protein with a predicted molecular weight of 73 kDa and is expressed in adult thymus, lung, brain, heart, and kidney. The N-terminal bHLH-PAS domain of this protein shares amino acid sequence identity with that of HIF1alpha and HIF2alpha (57% and 53% identity, respectively). The C-terminus of HIF3alpha contains a 36-amino acid sequence that shares 61% identity with the hypoxia responsive domain-1 (HRD1) of HIF1alpha. In transient transfections, this domain confers hypoxia responsiveness when linked to a heterologous transactivation domain. In vitro studies reveal that HIF3alpha dimerizes with a prototype beta-class subunit, ARNT, and that the resultant heterodimer recognizes the hypoxia responsive element (HRE) core sequence, TACGTG. Transient transfection experiments demonstrate that the HIF3alpha-ARNT interaction can occur in vivo, and that the activity of HIF3alpha is upregulated in response to cobalt chloride or low oxygen tension.
Figures


References
-
- Adams M. D.; Kelley J. M.; Gocayne J. D.; Dubnick M.; Polymeropoulos M. H.; Xiao H.; Merril C. R.; Wu A.; Olde B.; Moreno R. F.; Kerlavage A. R.; McCombie W. R.; Venter J. C. Complementary DNA sequencing: Expressed sequence tags and human genome project. Science 252:1651–1656; 1991. - PubMed
-
- Barik S.; Galinski M. S. “Megaprimer” method of PCR: Increased template concentration improves yield. Biotechniques 10:489–490; 1991. - PubMed
-
- Dolwick K. M.; Schmidt J. V.; Carver L. A.; Swanson H. I.; Bradfield C. A. Cloning and expression of a human Ah receptor cDNA. Mol. Pharmacol. 44:911–917; 1993. - PubMed
-
- Feinberg A. P.; Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal. Biochem. 132:6–13; 1983. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
