Mouse CD94/NKG2A is a natural killer cell receptor for the nonclassical major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I molecule Qa-1(b)
- PMID: 9815261
- PMCID: PMC2212405
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.188.10.1841
Mouse CD94/NKG2A is a natural killer cell receptor for the nonclassical major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I molecule Qa-1(b)
Abstract
Natural killer (NK) cells preferentially lyse targets that express reduced levels of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I proteins. To date, the only known mouse NK receptors for MHC class I belong to the Ly49 family of C-type lectin homodimers. Here, we report the cloning of mouse NKG2A, and demonstrate it forms an additional and distinct class I receptor, a CD94/NKG2A heterodimer. Using soluble tetramers of the nonclassical class I molecule Qa-1(b), we provide direct evidence that CD94/NKG2A recognizes Qa-1(b). We further demonstrate that NK recognition of Qa-1(b) results in the inhibition of target cell lysis. Inhibition appears to depend on the presence of Qdm, a Qa-1(b)-binding peptide derived from the signal sequences of some classical class I molecules. Mouse NKG2A maps adjacent to CD94 in the heart of the NK complex on mouse chromosome six, one of a small cluster of NKG2-like genes. Our findings suggest that mouse NK cells, like their human counterparts, use multiple mechanisms to survey class I expression on target cells.
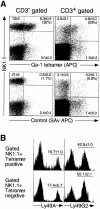
Figures




References
-
- Ehrlich R. Modulation of antigen processing and presentation by persistent virus infections and in tumors. Hum Immunol. 1997;54:104–116. - PubMed
-
- Ploegh HL. Viral strategies of immune evasion. Science. 1998;280:248–253. - PubMed
-
- Ljunggren HG, Karre K. In search of the ‘missing self': MHC molecules and NK cell recognition. Immunol Today. 1990;11:237–244. - PubMed
-
- Vance RE, Raulet DH. Toward a quantitative analysis of the repertoire of class I MHC-specific inhibitory receptors on natural killer cells. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1998;230:135–160. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

