PAT1, a new member of the GRAS family, is involved in phytochrome A signal transduction
- PMID: 10817761
- PMCID: PMC316623
PAT1, a new member of the GRAS family, is involved in phytochrome A signal transduction
Abstract
Light signaling via the phytochrome A (phyA) photoreceptor controls basic plant developmental processes including de-etiolation and hypocotyl elongation. We have identified a new Arabidopsis mutant, pat (phytochrome A signal transduction)1-1, which shows strongly reduced responses in continuous far-red light. Physiological and molecular data indicate that this mutant is disrupted at an early step of phyA signal transduction. The PAT1 gene encodes a cytoplasmic protein of 490 amino acids with sequence homologies to the plant-specific GRAS regulatory protein family. In the pat1-1 mutant, a T-DNA insertion introduces a premature stop codon, which likely results in the production of a truncated PAT1 protein of 341 amino acids. The semidominant phenotype of this mutant can be recapitulated by overexpression of an appropriately truncated PAT1 gene in the wild type. The results indicate that the truncated PAT1 protein acts in a dominant-negative fashion to inhibit phyA signaling.
Figures






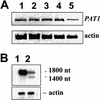
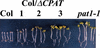

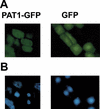
References
-
- Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990;215:403–410. - PubMed
-
- Barizza E, Lo Schiavo F, Terzi M, Filippini F. Evidence suggesting protein tyrosine phosphorylation in plants depends on the developmental conditions. FEBS Lett. 1999;447:191–194. - PubMed
-
- Barnes SA, Quaggio RB, Whitelam GC, Chua NH. fhy1 defines a branch point in phytochrome A signal transduction pathways for gene expression. Plant J. 1996b;10:1155–1161. - PubMed
-
- Bowler C, Neuhaus G, Yamagata H, Chua NH. Cyclic GMP and calcium mediate phytochrome phototransduction. Cell. 1994;77:73–81. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
