A mutation in the ovine cathepsin D gene causes a congenital lysosomal storage disease with profound neurodegeneration
- PMID: 10856224
- PMCID: PMC203370
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/19.12.2786
A mutation in the ovine cathepsin D gene causes a congenital lysosomal storage disease with profound neurodegeneration
Abstract
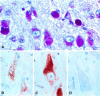
The neuronal ceroid lipofuscinoses (NCLs) constitute a group of neurodegenerative storage diseases characterized by progressive psychomotor retardation, blindness and premature death. Pathologically, there is accumulation of autofluorescent material in lysosome-derived organelles in a variety of cell types, but neurons in the central nervous system appear to be selectively affected and undergo progressive death. In this report we show that a novel form of NCL, congenital ovine NCL, is caused by a deficiency in the lysosomal aspartyl proteinase cathepsin D. A single nucleotide mutation in the cathepsin D gene results in conversion of an active site aspartate to asparagine, leading to production of an enzymatically inactive but stable protein. This results in severe cerebrocortical atrophy and early death, providing strong evidence for an important role of cathepsin D in neuronal development and/or homeostasis.
Figures


References
-
- Barohn R.J., Dowd,D.C. and Kagan-Hallet,K.S. (1992) Congenital ceroid-lipofuscinosis. Pediatr. Neurol., 8, 54–59. - PubMed
-
- Barrett A.J. and Kirschke,H. (1981) Cathepsin B, cathepsin H and cathepsin L. Methods Enzymol., 80, 535–561. - PubMed
-
- Barrett A.J., Rawlings,N.D. and Woessner,J.F.,Jr (eds) (1998) Handbook of Proteolytic Enzymes. Academic Press, London, UK.
-
- Camp L.A. and Hofmann,S.L. (1993) Purification and properties of a palmitoyl-protein thioesterase that cleaves palmitate from H-Ras. J. Biol. Chem., 268, 22566–22574. - PubMed
-
- Cataldo A.M., Barnett,J.L., Berman,S.A., Li,J., Quarless,S., Bursztajn,S., Lippa,C. and Nixon,R.A. (1995) Gene expression and cellular content of cathepsin D in Alzheimer’s disease brain: evidence for early up-regulation of the endosomal–lysosomal system. Neuron, 14, 671–680. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

