Genetic classification of "Rickettsia heilongjiangii" and "Rickettsia hulinii," two Chinese spotted fever group rickettsiae
- PMID: 10970415
- PMCID: PMC87418
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.38.9.3498-3501.2000
Genetic classification of "Rickettsia heilongjiangii" and "Rickettsia hulinii," two Chinese spotted fever group rickettsiae
Abstract
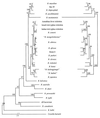
To determine the phylogenetic position of two new rickettsial strains isolated from ticks in China, 16S ribosomal DNA, gltA, and ompA (apart from the tandem repeat units) genes were amplified by PCR and sequenced. The phylogenetic relationships between these strains and other rickettsiae were inferred from the comparison of sequences of the three genes by the parsimony, neighbor-joining, and maximum-likelihood methods. The results demonstrated that the 054 strain, a rickettsia pathogenic in humans, and the HL-93 strain were related and clustered together with Rickettsia japonica. Significant statistical bootstrap values (100 and 92%) supported the nodes in this cluster. Based on previous genotypic and antigenic data and the phylogenetic analysis presented here, the 054 and HL-93 strains should be considered as new species, and we formally propose that they be named "Rickettsia heilongjiangii" and "Rickettsia hulinii," respectively.
Figures
References
-
- Chen M, Fan M Y, Bi D Z, Zhang J Z. Sequence analysis of a fragment of rOmpA gene of several isolates of spotted fever group rickettsiae from China. Acta Virol. 1998;42:91–93. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

