Molecular characterization of multidrug-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae isolates in Korea. The Asian Network for Surveillance of Resistant Pathogens (ANSORP) Study Group
- PMID: 10747158
- PMCID: PMC86510
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.38.4.1641-1644.2000
Molecular characterization of multidrug-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae isolates in Korea. The Asian Network for Surveillance of Resistant Pathogens (ANSORP) Study Group
Abstract
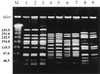
Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis, ribotyping, and fingerprinting analysis of 22 invasive isolates of multidrug-resistant (MDR) pneumococci from Korea showed that 59 to 82% were genetically related. DNA sequencing of the PBP 2B gene showed relatively uniform alterations in nucleotides (5.4 to 7.8%) and amino acids (3.0 to 4. 3%), while Asn-276-->Lys, Arg-285-->Cys and Ser-305-->Phe substitutions were unique to Korean MDR strains, suggesting the spread of a few epidemic clones of resistant pneumococci within Korea.
Figures

References
-
- Appelbaum P C. Antimicrobial resistance in Streptococcus pneumoniae: an overview. Clin Infect Dis. 1992;15:77–83. - PubMed
-
- Chong Y, Lee K, Kwon O H, Henrichsen J. Capsular types and antimicrobial resistance of Streptococcus pneumoniae isolated in Korea. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1995;14:528–531. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

