Biosynthesis of terpenoids: 4-diphosphocytidyl-2C-methyl-D-erythritol synthase of Arabidopsis thaliana
- PMID: 10841550
- PMCID: PMC18623
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.97.12.6451
Biosynthesis of terpenoids: 4-diphosphocytidyl-2C-methyl-D-erythritol synthase of Arabidopsis thaliana
Abstract
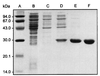
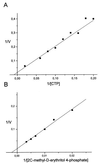
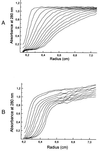
A hypothetical gene with similarity to the ispD gene of Escherichia coli was cloned from Arabidopsis thaliana cDNA. The ORF of 909 bp specifies a protein of 302 amino acid residues. The cognate chromosomal gene consists of 2,071 bp and comprises 11 introns with a size range of 78-202 bp. A fragment comprising amino acid residues 76-302 was expressed in a recombinant E. coli strain. The protein was purified to homogeneity and was shown to catalyze the formation of 4-diphosphocytidyl-2C-methyl-d-erythritol from 2C-methyl-d-erythritol 4-phosphate with a specific activity of 67 micromol small middle dotmin(-1) mg(-1). The Michaelis constants for 4-diphosphocytidyl-2C-methyl-d-erythritol and CTP were 500 microM and 114 microM, respectively.
Figures

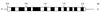



References
-
- Broers S T J. Ph.D. thesis. Zürich, Switzerland: Eidgenössiche Technische Hochschule; 1994.
-
- Eisenreich W, Schwarz M, Cartayrade A, Arigoni D, Zenk M, Bacher A. Chem Biol. 1998;5:R221–R233. - PubMed
-
- Rohmer M. In: Comprehensive Natural Products Chemistry. Barton D, Nakanishi K, editors. Vol. 2. Oxford: Pergamon; 1999. pp. 45–68.
-
- Schwarz M K. Ph.D. thesis. Zürich, Switzerland: Eidgenössiche Technische Hochschule; 1994.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

