Analysis of the 5S RNA pool in Arabidopsis thaliana: RNAs are heterogeneous and only two of the genomic 5S loci produce mature 5S RNA
- PMID: 11779838
- PMCID: PMC155267
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.181301
Analysis of the 5S RNA pool in Arabidopsis thaliana: RNAs are heterogeneous and only two of the genomic 5S loci produce mature 5S RNA
Abstract
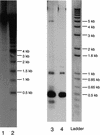
One major 5S RNA, 120 bases long, was revealed by an analysis of mature 5S RNA from tissues, developmental stages, and polysomes in Arabidopsis thaliana. Minor 5S RNA were also found, varying from the major one by one or two base substitutions; 5S rDNA units from each 5S array of the Arabidopsis genome were isolated by PCR using CIC yeast artificial chromosomes (YACs) mapped on the different loci. By using a comparison of the 5S DNA and RNA sequences, we could show that both major and minor 5S transcripts come from only two of the genomic 5S loci: chromosome 4 and chromosome 5 major block. Other 5S loci are either not transcribed or produce rapidly degraded 5S transcripts. Analysis of the 5'- and 3'-DNA flanking sequence has permitted the definition of specific signatures for each 5S rDNA array.
Figures







References
-
- AGI. Analysis of the genome sequence of the flowering plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature. 2000a;408:796–815. - PubMed
-
- AGI. Sequence and analysis of chromosome 3 of the plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature. 2000b;408:820–822. - PubMed
-
- AGI. Sequence and analysis of chromosome 5 of the plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature. 2000c;408:823–826. - PubMed
-
- Agarwal ML, Aldrich J, Agarwal A, Cullis CA. The flax ribosomal RNA-encoding genes are arranged in tandem at a single locus interspersed by “non-rDNA” sequences. Gene. 1992;120:151–156. - PubMed
-
- Appels R, Gerlach WL, Dennis ES, Swift H, Peacock W J. Molecular and chromosomal organization of DNA sequences coding for the ribosomal RNAs in cereals. Chromosoma. 1980;78:293–311.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
