US11 of herpes simplex virus type 1 interacts with HIPK2 and antagonizes HIPK2-induced cell growth arrest
- PMID: 14990717
- PMCID: PMC353731
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.78.6.2984-2993.2004
US11 of herpes simplex virus type 1 interacts with HIPK2 and antagonizes HIPK2-induced cell growth arrest
Abstract
Homeodomain-interacting protein kinase 2 (HIPK2) is a nuclear serine/threonine kinase of the subfamily of dual-specificity Yak1-related kinase proteins. HIPK2 was first described as a homeodomain-interacting protein kinase acting as a corepressor for homeodomain transcription factors. More recently, it was reported that HIPK2 plays a role in p53-mediated cellular apoptosis and could also participate in the regulation of the cell cycle. US11 protein of herpes simplex virus type 1 is a multifunctional protein involved in the regulation of several processes related to the survival of cells submitted to environmental stresses by mechanisms that are not fully elucidated. In an attempt to better understand the multiple functions of US11, we identified cellular binding partners of this protein by using the yeast two-hybrid system. We report that US11 interacts with HIPK2 through the PEST domain of HIPK2 and that this interaction occurs also in human cells. This interaction modifies the subcellular distribution of HIPK2 and protects the cell against the HIPK2-induced cell growth arrest.
Figures
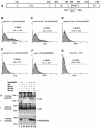
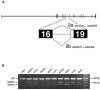
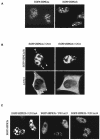

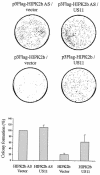
References
-
- Besse, S., J.-J. Diaz, E. Pichard, K. Kindbeiter, J.-J. Madjar, and F. Puvion-Dutilleul. 1996. In situ hybridization and immuno-electron microscope analyses of the Us11 gene of herpes simplex virus type 1 during transient expression. Chromosoma 104:434-444. - PubMed
-
- Brown, S. M., and J. Harland. 1987. Three mutants of herpes simplex virus type 2: one lacking the genes Us10, Us11, Us12 and two in which Rs has been extended by 6 kb to 0, 91 map units with loss of Us sequences between 0, 94 and the Us/TRs junction. J. Gen. Virol. 68:1-18. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

