Wide spectrum of tumors in knock-in mice carrying a Cdk4 protein insensitive to INK4 inhibitors
- PMID: 11726500
- PMCID: PMC125323
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/20.23.6637
Wide spectrum of tumors in knock-in mice carrying a Cdk4 protein insensitive to INK4 inhibitors
Abstract
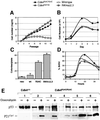
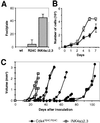
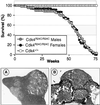
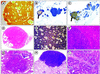
We have introduced a point mutation in the first coding exon of the locus encoding the cyclin-dependent kinase 4 (Cdk4) by homologous recombination in embryonic stem cells. This mutation (replacement of Arg24 by Cys) was first found in patients with hereditary melanoma and renders Cdk4 insensitive to INK4 inhibitors. Here, we report that primary embryonic fibroblasts expressing the mutant Cdk4R24C kinase are immortal and susceptible to transformation by Ras oncogenes. Moreover, homozygous Cdk4(R24C/R24C) mutant mice develop multiple tumors with almost complete penetrance. The most common neoplasia (endocrine tumors and hemangiosarcomas) are similar to those found in pRb(+/-) and p53(-/-) mice. This Cdk4 mutation cooperates with p53 and p27(Kip1) deficiencies in decreasing tumor latency and favoring development of specific tumor types. These results provide experimental evidence for a central role of Cdk4 regulation in cancer and provide a valuable model for testing the potential anti-tumor effect of Cdk4 inhibitors in vivo.
Figures

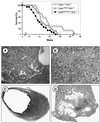
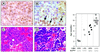
References
-
- Brooks G. and La Thangue,N.B. (1999) The cell cycle and drug discovery: the promise and the hope. Drug Discov. Today, 5, 455–464. - PubMed
-
- Corcoran M.M. et al. (1999) Disregulation of cyclin dependent kinase 6 expression in splenic marginal zone lymphoma through chromosome 7q translocations. Oncogene, 18, 6271–6277. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

