Isolation and initial characterization of a bacterial consortium able to mineralize fluorobenzene
- PMID: 11772615
- PMCID: PMC126581
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.68.1.102-105.2002
Isolation and initial characterization of a bacterial consortium able to mineralize fluorobenzene
Abstract
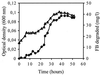
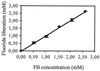
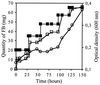
Fluorinated compounds are known to be more resistant to microbial degradation than other halogenated chemicals. A microbial consortium capable of aerobic biodegradation of fluorobenzene (FB) as the sole source of carbon and energy was isolated by selective enrichment from sediments collected in a drain near an industrial site. A combination of three microbial strains recovered from the enriched consortium was shown to be necessary for complete FB mineralization. Two of the strains (F1 and F3) were classified by 16S rRNA analysis as belonging to the Sphingobacterium/Flavobacterium group, while the third (F4) falls in the beta-Proteobacteria group, clustering with Alcaligenes species. Strain F4 was consistently found in the liquid cultures in a much greater proportion than strains F1 and F3 (86:8:6 for F4, F1, and F3, respectively). Stoichiometric release of fluoride ions was measured in batch and fed-batch cultures. In batch cultures, the consortium was able to use FB up to concentrations of 400 mg liter(-1) and was able to utilize a range of other organic compounds, including 4-fluorophenol and 4-fluorobenzoate. To our knowledge this is the first time biodegradation of FB as a sole carbon source has been reported.
Figures
References
-
- Boersma, M. G., T. Y. Dinarieva, W. J. Middelhoven, W. J. W. Van Berkel, J. Doran, J. Vervoort, and I. M. C. M. Rietjens. 1998. 19F nuclear magnetic resonance as a tool to investigate microbial degradation of fluorophenols to fluorocathecols and fluoromuconates. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 64:1256–1263. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bondar, V. S., M. G. Boersma, E. L. Golovlev, J. Vervoort, W. J. H. Van Berkel, Z. I. Finkelstein, I. P. Solyanikova, L. A. Golovleva, and I. M. C. M. Rietjens. 1998. 19F NMR study on the biodegradation of fluorophenols by various Rhodococcus species. Biodegradation 9:475–486. - PubMed
-
- Caldeira, M., S. C. Heald, M. F. Carvalho, A. T. Bull, I. Vasconcelos, and P. M. L. Castro. 1999. 4-Chlorophenol degradation by a bacterial consortium: development of a granular activated carbon biofilm reactor. Appl. Microb. Biotechnol. 52:722–729. - PubMed
-
- Cass, A. E. G., D. W. Ribbons, J. R. Rossiter, and S. B. Williams. 1987. Biotransformation of aromatic compounds. Monitoring fluorinated analogues by NMR. FEBS Lett. 22:353–357. - PubMed
-
- Clement, P., V. Matus, L. Cardenas, and B. Gonzalez. 1995. Degradation of trichlorophenols by Alcaligenes eutrophus JMP134. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 127:51–55. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

