Endogenous and silencing-associated small RNAs in plants
- PMID: 12119378
- PMCID: PMC150710
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.003210
Endogenous and silencing-associated small RNAs in plants
Abstract
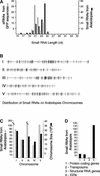
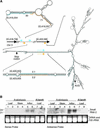
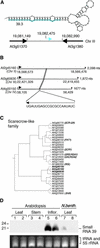
A large set of endogenous small RNAs of predominantly 21 to 24 nucleotides was identified in Arabidopsis. These small RNAs resembled micro-RNAs from animals and were similar in size to small interfering RNAs that accumulated during RNA silencing triggered by multiple types of inducers. Among the 125 sequences identified, the vast majority (90%) arose from intergenic regions, although small RNAs corresponding to predicted protein-coding genes, transposon-like sequences, and a structural RNA gene also were identified. Evidence consistent with the derivation of small RNAs of both polarities, and from highly base-paired precursors, was obtained through the identification and analysis of clusters of small RNA loci. The accumulation of specific small RNAs was regulated developmentally. We propose that Arabidopsis small RNAs participate in a wide range of post-transcriptional and epigenetic events.
Figures




References
-
- Ambros, V. (2000). Control of developmental timing in Caenorhabditis elegans. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 10, 428–433. - PubMed
-
- Ambros, V., and Horvitz, H.R. (1984). Heterochronic mutants of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Science 226, 409–416. - PubMed
-
- Arabidopsis Genome Initiative. (2000). Analysis of the genome sequence of the flowering plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature 408, 796–815. - PubMed
-
- Banerjee, D., and Slack, F. (2002). Control of developmental timing by small temporal RNAs: A paradigm for RNA-mediated regulation of gene expression. Bioessays 24, 119–129. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

