Secretory low molecular weight phospholipase A2 plays important roles in cell elongation and shoot gravitropism in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 12953106
- PMCID: PMC181326
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.014423
Secretory low molecular weight phospholipase A2 plays important roles in cell elongation and shoot gravitropism in Arabidopsis
Abstract
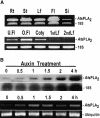
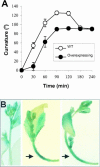
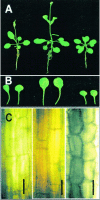
To elucidate the cellular functions of phospholipase A(2) in plants, an Arabidopsis cDNA encoding a secretory low molecular weight phospholipase A(2) (AtsPLA(2)beta) was isolated. Phenotype analyses of transgenic plants showed that overexpression of AtsPLA(2)beta promotes cell elongation, resulting in prolonged leaf petioles and inflorescence stems, whereas RNA interference-mediated silencing of AtsPLA(2)beta expression retards cell elongation, resulting in shortened leaf petioles and stems. AtsPLA(2)beta is expressed in the cortical, vascular, and endodermal cells of the actively growing tissues of inflorescence stems and hypocotyls. AtsPLA(2)beta then is secreted into the extracellular spaces, where signaling for cell wall acidification is thought to occur. AtsPLA(2)beta-overexpressing or -silenced transgenic plants showed altered gravitropism in inflorescence stems and hypocotyls. AtsPLA(2)beta expression is induced rapidly by auxin treatment and in the curving regions of inflorescence stems undergoing the gravitropic response. These results suggest that AtsPLA(2)beta regulates the process of cell elongation and plays important roles in shoot gravitropism by mediating auxin-induced cell elongation.
Figures





References
-
- Bechtold, N., and Pelletier, G. (1998). In planta Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of adult Arabidopsis thaliana plants by vacuum infiltration. Methods Mol. Biol. 82, 259–266. - PubMed
-
- Boonsirichai, K., Guan, C., Chen, R., and Masson, P.H. (2002). Root gravitropism: An experimental tool to investigate basic cellular and molecular processes underlying mechanosensing and signal transmission in plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 53, 421–447. - PubMed
-
- Chapman, K.D. (1998). Phospholipase activity during plant growth and development and in response to environmental stress. Trends Plant Sci. 3, 419–426.
-
- Clough, S.J., and Bent, A.F. (1998). Floral dip: A simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 16, 735–743. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

