Detection of Verrucomicrobia in a pasture soil by PCR-mediated amplification of 16S rRNA genes
- PMID: 10473454
- PMCID: PMC99779
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.65.9.4280-4284.1999
Detection of Verrucomicrobia in a pasture soil by PCR-mediated amplification of 16S rRNA genes
Abstract
Oligonucleotide primers were designed and used to amplify, by PCR, partial 16S rRNA genes of members of the bacterial division Verrucomicrobia in DNA extracted from a pasture soil. By applying most-probable-number theory to the assay, verrucomicrobia appeared to contribute some 0.2% of the soil DNA. Amplified ribosomal DNA restriction analysis of 53 cloned PCR-amplified partial 16S rRNA gene fragments and comparative sequence analysis of 21 nonchimeric partial 16S rRNA genes showed that these primers amplified only 16S rRNA genes of members of the Verrucomicrobia in DNA extracted from the soil.
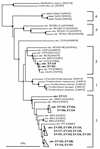
Figures

References
-
- Altschul S F, Gish W, Miller W, Myers E W, Lipman D J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990;215:403–410. - PubMed
-
- Beliaeff B, Mary J Y. The “most probable number” estimate and its confidence limits. Water Res. 1993;27:799–805.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

