The serine/arginine-rich protein family in rice plays important roles in constitutive and alternative splicing of pre-mRNA
- PMID: 16339852
- PMCID: PMC1323490
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.105.037069
The serine/arginine-rich protein family in rice plays important roles in constitutive and alternative splicing of pre-mRNA
Abstract
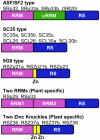
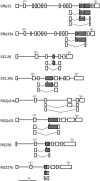
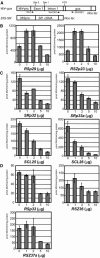
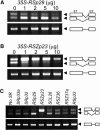
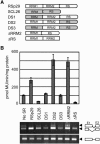
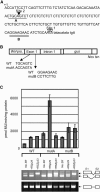
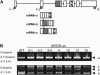
Ser/Arg-rich (SR) proteins play important roles in the constitutive and alternative splicing of pre-mRNA. We isolated 20 rice (Oryza sativa) genes encoding SR proteins, of which six contain plant-specific characteristics. To determine whether SR proteins modulate splicing efficiency and alternative splicing of pre-mRNA in rice, we used transient assays in rice protoplasts by cotransformation of SR protein genes with the rice Waxy(b) (Wx(b))-beta-glucuronidase fusion gene. The results showed that plant-specific RSp29 and RSZp23, an SR protein homologous to human 9G8, enhanced splicing and altered the alternative 5' splice sites of Wx(b) intron 1. The resulting splicing pattern was unique to each SR protein; RSp29 stimulated splicing at the distal site, and RSZp23 enhanced splicing at the proximal site. Results of domain-swapping experiments between plant-specific RSp29 and SCL26, which is a homolog of human SC35, showed the importance of RNA recognition motif 1 and the Arg/Ser-rich (RS) domain for the enhancement of splicing efficiencies. Overexpression of plant-specific RSZ36 and SRp33b, a homolog of human ASF/SF2, in transgenic rice changed the alternative splicing patterns of their own pre-mRNAs and those of other SR proteins. These results show that SR proteins play important roles in constitutive and alternative splicing of rice pre-mRNA.
Figures


References
-
- Ali, G.S., Golovkin, M., and Reddy, A.S. (2003). Nuclear localization and in vivo dynamics of a plant-specific serine/arginine-rich protein. Plant J. 36 883–893. - PubMed
-
- Black, D.L. (2003). Mechanisms of alternative pre-messenger RNA splicing. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 72 291–336. - PubMed
-
- Cai, X.L., Wang, Z.Y., Xing, Y.Y., Zhang, J.L., and Hong, M.M. (1998). Aberrant splicing of intron 1 leads to the heterogeneous 5′ UTR and decreased expression of waxy gene in rice cultivars of intermediate amylose content. Plant J. 14 459–465. - PubMed
-
- Cartegni, L., Chew, S.L., and Krainer, A.R. (2002). Listening to silence and understanding nonsense: Exonic mutations that affect splicing. Nat. Rev. Genet. 3 285–298. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

