Disruption of the serine/threonine kinase 9 gene causes severe X-linked infantile spasms and mental retardation
- PMID: 12736870
- PMCID: PMC1180301
- DOI: 10.1086/375538
Disruption of the serine/threonine kinase 9 gene causes severe X-linked infantile spasms and mental retardation
Abstract
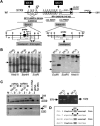
X-linked West syndrome, also called "X-linked infantile spasms" (ISSX), is characterized by early-onset generalized seizures, hypsarrhythmia, and mental retardation. Recently, we have shown that the majority of the X-linked families with infantile spasms carry mutations in the aristaless-related homeobox gene (ARX), which maps to the Xp21.3-p22.1 interval, and that the clinical picture in these patients can vary from mild mental retardation to severe ISSX with additional neurological abnormalities. Here, we report a study of two severely affected female patients with apparently de novo balanced X;autosome translocations, both disrupting the serine-threonine kinase 9 (STK9) gene, which maps distal to ARX in the Xp22.3 region. We show that STK9 is subject to X-inactivation in normal female somatic cells and is functionally absent in the two patients, because of preferential inactivation of the normal X. Disruption of the same gene in two unrelated patients who have identical phenotypes (consisting of early-onset severe infantile spasms, profound global developmental arrest, hypsarrhythmia, and severe mental retardation) strongly suggests that lack of functional STK9 protein causes severe ISSX and that STK9 is a second X-chromosomal locus for this disorder.
Figures

References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- Ensembl Genome Browser, http://www.ensembl.org/
-
- GenBank, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Genbank/ (for STK9 mRNA sequences [accession numbers AY217744, Y15057, BC010966, BC036091, BF679133, AL704691, and BI559845] and STK9 genomic sequences [accession numbers AL109798, Z925542, and Z93023])
-
- Mendelian Cytogenetic Network (MCN) Reference Center at the Max-Planck-Institute for Molecular Genetics, http://www.molgen.mpg.de/~cytogen/
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/ (for ISSX, GLI3, and INHBA)
References
-
- Bienvenu T, Poirier K, Friocourt G, Bahi N, Beaumont D, Fauchereau F, Ben Jeema L, Zemni R, Vinet MC, Francis F, Couvert P, Gomot M, Moraine C, van Bokhoven H, Kalscheuer V, Frints S, Gécz J, Ohzaki K, Chaabouni H, Fryns JP, Desportes V, Beldjord C, Chelly J (2002) ARX, a novel Prd-class-homeobox gene highly expressed in the telencephalon, is mutated in X-linked mental retardation. Hum Mol Genet 11:981–991 - PubMed
-
- Bruyere H, Lewis, SE, Wood S, MacLeod PJ, Langlois S (1999) Confirmation of linkage in X-linked infantile spasms (West syndrome) and refinement of the disease locus to Xp21.3-Xp22.1. Clin Genet 55:173–182 - PubMed
-
- Claes S, Devriendt K, Lagae L, Ceulemans C, Dom L, Casaer P, Raeymaekers P, Cassiman JJ, Fryns JP (1997) The X-linked infantile spasms syndrome (MIM 308350) maps to Xp11.4-Xpter in two pedigrees. Ann Neurol 42:360–364 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

