Mutation of melanosome protein RAB38 in chocolate mice
- PMID: 11917121
- PMCID: PMC123672
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.072087599
Mutation of melanosome protein RAB38 in chocolate mice
Abstract
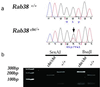
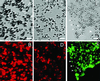
Mutations of genes needed for melanocyte function can result in oculocutaneous albinism. Examination of similarities in human gene expression patterns by using microarray analysis reveals that RAB38, a small GTP binding protein, demonstrates a similar expression profile to melanocytic genes. Comparative genomic analysis localizes human RAB38 to the mouse chocolate (cht) locus. A G146T mutation occurs in the conserved GTP binding domain of RAB38 in cht mice. Rab38(cht)/Rab38(cht) mice exhibit a brown coat similar in color to mice with a mutation in tyrosinase-related protein 1 (Tyrp1), a mouse model for oculocutaneous albinism. The targeting of TYRP1 protein to the melanosome is impaired in Rab38(cht)/Rab38(cht) melanocytes. These observations, and the fact that green fluorescent protein-tagged RAB38 colocalizes with end-stage melanosomes in wild-type melanocytes, suggest that RAB38 plays a role in the sorting of TYRP1. This study demonstrates the utility of expression profile analysis to identify mammalian disease genes.
Figures





References
-
- Jackson I J. Hum Mol Genet. 1997;6:1613–1624. - PubMed
-
- King R A, Hearing V J, Creel D, Oetting W S. In: The Metabolic Basis of Inherited Disease. 7th Ed. Scriver C R, Beaudet A L, Sly W S, Valle D V, editors. New York: McGraw–Hill; 1995. pp. 4353–4392.
-
- Marks M S, Seabra M C. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2001;2:738–748. - PubMed
-
- Loftus S K, Pavan W J. Pigment Cell Res. 2000;13:141–146. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

