Nef proteins from simian immunodeficiency virus-infected chimpanzees interact with p21-activated kinase 2 and modulate cell surface expression of various human receptors
- PMID: 15194762
- PMCID: PMC421647
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.78.13.6864-6874.2004
Nef proteins from simian immunodeficiency virus-infected chimpanzees interact with p21-activated kinase 2 and modulate cell surface expression of various human receptors
Abstract
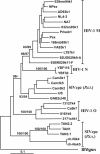
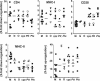
The accessory Nef protein allows human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) to persist at high levels and to cause AIDS in infected humans. The function of HIV-1 group M subtype B nef alleles has been extensively studied, and a variety of in vitro activities believed to be important for viral pathogenesis have been established. However, the function of nef alleles derived from naturally simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV)-infected chimpanzees, the original host of HIV-1, or from the HIV-1 N and O groups resulting from independent zoonotic transmissions remains to be investigated. In the present study we demonstrate that SIVcpz and HIV-1 group N or O nef alleles down-modulate CD4, CD28, and class I or II MHC molecules and up-regulate surface expression of the invariant chain (Ii) associated with immature major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II. Furthermore, the ability of Nef to interact with the p21-activated kinase 2 was generally conserved. The functional activity of HIV-1 group N and O nef genes did not differ significantly from group M nef alleles. However, SIVcpz nef genes as a group showed a 1.8- and 2.0-fold-higher activity in modulating CD28 (P = 0.0002) and Ii (P = 0.016) surface expression, respectively, but were 1.7-fold less active in down-regulating MHC class II molecules (P = 0.006) compared to HIV-1 M nef genes. Our finding that primary SIVcpz nef alleles derived from naturally infected chimpanzees modulate the surface expression of various human cellular receptors involved in T-cell activation and antigen presentation suggests that functional nef genes helped the chimpanzee virus to persist efficiently in infected humans immediately after zoonotic transmission.
Figures



References
-
- Aiken, C., J. Konner, N. R. Landau, M. E. Lenburg, and D. Trono. 1994. Nef induces CD4 endocytosis: requirement for a critical dileucine motif in the membrane-proximal CD4 cytoplasmic domain. Cell 76:853-864. - PubMed
-
- Arganaraz, E. R., M. Schindler, F. Kirchhoff, M. J. Cortes, and J. Lama. 2003. Enhanced CD4 down-modulation by late-stage HIV-1 nef alleles is associated with increased Env incorporation and viral replication. J. Biol. Chem. 278:33912-33919. - PubMed
-
- Ayouba, A., S. Souquieres, B. Njinku, P. M. Martin, M. C. Muller-Trutwin, P. Roques, F. Barre-Sinoussi, P. Mauclere, F. Simon, and E. Nerrienet. 2000. HIV-1 group N among HIV-1-seropositive individuals in Cameroon. AIDS 14:2623-2625. - PubMed
-
- Bailes, E., R. R. Chaudhuri, M. L. Santiago, F. Bibollet-Ruche, B. H. Hahn, and P. M. Sharp. 2002. The evolution of primate lentiviruses and the origins of AIDS, p. 65-96. In T. Leitner (ed.), The molecular epidemiology of human viruses. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Norwell, Mass.
-
- Bailes, E., F. Gao, F. Bibollet-Ruche, V. Courgnaud, M. Peeters, P. A. Marx, B. H. Hahn, and P. M. Sharp. 2003. Hybrid origin of SIV in chimpanzees. Science 300:1713. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

