Developmentally restricted genetic determinants of human arsenic metabolism: association between urinary methylated arsenic and CYT19 polymorphisms in children
- PMID: 15929903
- PMCID: PMC1257606
- DOI: 10.1289/ehp.7780
Developmentally restricted genetic determinants of human arsenic metabolism: association between urinary methylated arsenic and CYT19 polymorphisms in children
Abstract
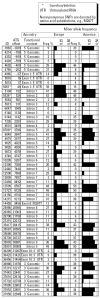
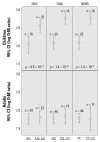
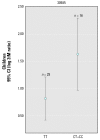
We report the results of a screen for genetic association with urinary arsenic metabolite levels in three arsenic metabolism candidate genes, PNP, GSTO, and CYT19, in 135 arsenic-exposed subjects from the Yaqui Valley in Sonora, Mexico, who were exposed to drinking water concentrations ranging from 5.5 to 43.3 ppb. We chose 23 polymorphic sites to test in the arsenic-exposed population. Initial phenotypes evaluated included the ratio of urinary inorganic arsenic(III) to inorganic arsenic(V) and the ratio of urinary dimethylarsenic(V) to monomethylarsenic(V) (D:M). In the initial association screening, three polymorphic sites in the CYT19 gene were significantly associated with D:M ratios in the total population. Subsequent analysis of this association revealed that the association signal for the entire population was actually caused by an extremely strong association in only the children (7-11 years of age) between CYT19 genotype and D:M levels. With children removed from the analysis, no significant genetic association was observed in adults (18-79 years). The existence of a strong, developmentally regulated genetic association between CYT19 and arsenic metabolism carries import for both arsenic pharmacogenetics and arsenic toxicology, as well as for public health and governmental regulatory officials.
Figures
References
-
- Calleja EM, Warrell RP., Jr Differentiating agents in pediatric malignancies: all-transretinoic acid and arsenic in acute promyelocytic leukemia. Curr Oncol Rep. 2000;2(6):519–523. - PubMed
-
- Chowdhury UK, Rahman MM, Sengupta MK, Lodh D, Chanda CR, Roy S, et al. Pattern of excretion of arsenic compounds [arsenite, arsenate, MMA(V), DMA(V)] in urine of children compared to adults from an arsenic exposed area in Bangladesh. J Environ Sci Health A Tox Hazard Subst Environ Eng. 2003;38(1):87–113. - PubMed
-
- Devlin B, Risch N. A comparison of linkage disequilibrium measures for fine-scale mapping. Genomics. 1995;29(2):311–322. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

