SARS-CoV-2 viral load is associated with increased disease severity and mortality
- PMID: 33127906
- PMCID: PMC7603483
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-19057-5
SARS-CoV-2 viral load is associated with increased disease severity and mortality
Abstract
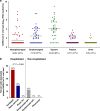
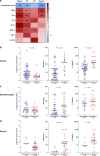
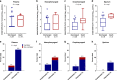
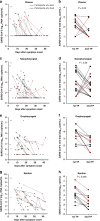
The relationship between SARS-CoV-2 viral load and risk of disease progression remains largely undefined in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Here, we quantify SARS-CoV-2 viral load from participants with a diverse range of COVID-19 disease severity, including those requiring hospitalization, outpatients with mild disease, and individuals with resolved infection. We detected SARS-CoV-2 plasma RNA in 27% of hospitalized participants, and 13% of outpatients diagnosed with COVID-19. Amongst the participants hospitalized with COVID-19, we report that a higher prevalence of detectable SARS-CoV-2 plasma viral load is associated with worse respiratory disease severity, lower absolute lymphocyte counts, and increased markers of inflammation, including C-reactive protein and IL-6. SARS-CoV-2 viral loads, especially plasma viremia, are associated with increased risk of mortality. Our data show that SARS-CoV-2 viral loads may aid in the risk stratification of patients with COVID-19, and therefore its role in disease pathogenesis should be further explored.
Conflict of interest statement
J.Z.L. has consulted for Abbvie and Jan Biotech. G.A. is the founder of Seromyx Inc. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- He, X. et al. Temporal dynamics in viral shedding and transmissibility of COVID-19. Nat. Med.10.1038/s41591-020-0869-5 (2020). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- T32 AI007387/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI135995/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002541/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI080289/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CK000490/CK/NCEZID CDC HHS/United States
- K08 HL141694/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI106701/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI060354/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- R01 HL142093/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01CK000490/ACL/ACL HHS/United States
- K08 DK114563/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

