Treatment of Middle East Respiratory Syndrome with a combination of lopinavir-ritonavir and interferon-β1b (MIRACLE trial): study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 29382391
- PMCID: PMC5791210
- DOI: 10.1186/s13063-017-2427-0
Treatment of Middle East Respiratory Syndrome with a combination of lopinavir-ritonavir and interferon-β1b (MIRACLE trial): study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: It had been more than 5 years since the first case of Middle East Respiratory Syndrome coronavirus infection (MERS-CoV) was recorded, but no specific treatment has been investigated in randomized clinical trials. Results from in vitro and animal studies suggest that a combination of lopinavir/ritonavir and interferon-β1b (IFN-β1b) may be effective against MERS-CoV. The aim of this study is to investigate the efficacy of treatment with a combination of lopinavir/ritonavir and recombinant IFN-β1b provided with standard supportive care, compared to treatment with placebo provided with standard supportive care in patients with laboratory-confirmed MERS requiring hospital admission.
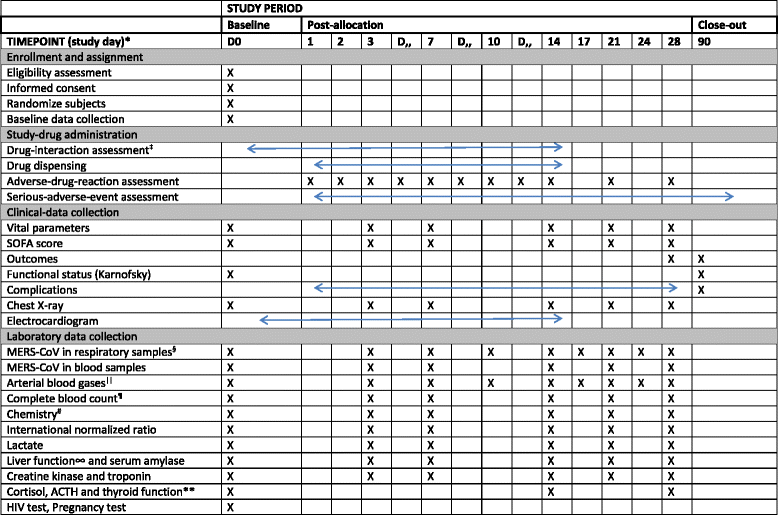
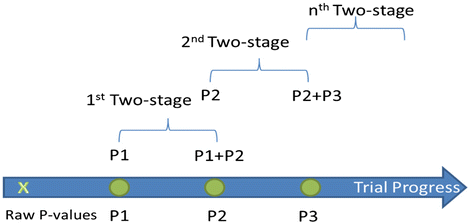
Methods: The protocol is prepared in accordance with the SPIRIT (Standard Protocol Items: Recommendations for Interventional Trials) guidelines. Hospitalized adult patients with laboratory-confirmed MERS will be enrolled in this recursive, two-stage, group sequential, multicenter, placebo-controlled, double-blind randomized controlled trial. The trial is initially designed to include 2 two-stage components. The first two-stage component is designed to adjust sample size and determine futility stopping, but not efficacy stopping. The second two-stage component is designed to determine efficacy stopping and possibly readjustment of sample size. The primary outcome is 90-day mortality.
Discussion: This will be the first randomized controlled trial of a potential treatment for MERS. The study is sponsored by King Abdullah International Medical Research Center, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. Enrollment for this study began in November 2016, and has enrolled thirteen patients as of Jan 24-2018.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov, ID: NCT02845843 . Registered on 27 July 2016.
Keywords: Antiviral; Clinical trial; Coronavirus; Interferon-β1b; Lopinavir/ritonavir; MERS; Saudi Arabia.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The MIRACLE study is approved by the Scientific Committee and the Institutional Review Board at King Abdulaziz Medical City (RC15/142) and registered at the Saudi Food and Drug Authority (SFDA). The approval of the Ethics Committees and the SFDA will be secured from each participated sites before starting patient recruitment. Patients who meet the eligibility criteria or substitute decision-makers (for patients lacking decision-making capacity) of eligible patients will be approached to obtain informed consent for enrollment.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization: Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV). http://www.who.int/emergencies/mers-cov/en/. Accessed 14 Jan 2018.
-
- Falzarano D, de Wit E, Rasmussen AL, Feldmann F, Okumura A, Scott DP, Brining D, Bushmaker T, Martellaro C, Baseler L, et al. Treatment with interferon-alpha2b and ribavirin improves outcome in MERS-CoV-infected rhesus macaques. Nat Med. 2013;19(10):1313–7. doi: 10.1038/nm.3362. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

