Microvirga massiliensis sp. nov., the human commensal with the largest genome
- PMID: 26749561
- PMCID: PMC4831475
- DOI: 10.1002/mbo3.329
Microvirga massiliensis sp. nov., the human commensal with the largest genome
Abstract
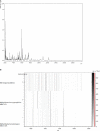
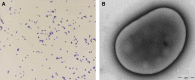
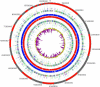
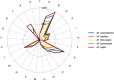
Microvirga massiliensis sp. nov. strain JC119(T) is a bacteria isolated in Marseille from a stool sample collected in Senegal. The 16S rRNA (JF824802) of M. massiliensis JC119(T) revealed 95% sequence identity with Microvirga lotononidis WSM3557(T) (HM362432). This bacterium is aerobic, gram negative, catalase positive, and oxidase negative. The draft genome of M. massiliensis JC119(T) comprises a 9,207,211-bp-long genome that is the largest bacterial genome of an isolate in humans. The genome exhibits a G+C content of 63.28% and contains 8685 protein-coding genes and 77 RNA genes, including 21 rRNA genes. Here, we describe the features of M. massiliensis JC119(T), together with the genome sequence information and its annotation.
Keywords: Culturomics; Microvirga massiliensis; large genome; taxonogenomics.
© 2016 The Authors. MicrobiologyOpen published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- Adler, J. , and Margaret M. D.. 1967. A method for measuring the motility of bacteria and for comparing random and non‐random motility. Microbiology 46:161–173. - PubMed
-
- Aken, B. V. , Peres C. M., Lafferty Doty S., Moon Yoon J., and Schnoor J. L.. 2004. Methylobacterium populi sp. nov., a novel aerobic, pink‐pigmented, facultatively methylotrophic, methane‐utilizing bacterium isolated from poplar trees (Populus deltoides×nigra DN34). Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 54:1191–1196. - PubMed
-
- Altschul, S. F. , Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., and Lipman D. J.. 1990. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 215:403–410. - PubMed
-
- Angelakis, E. , Armougom F., Million M., and Raoult D.. 2012. The relationship between gut microbiota and weight gain in humans. Future Microbiol. 7:91–109. - PubMed
-
- Ardley, J. K. , Parker M. A., De Meyer S. E., Trengove R. D., O'Hara G. W., Reeve W. G., et al. 2012. Microvirga lupini sp. nov., Microvirga lotononidis sp. nov. and Microvirga zambiensis sp. nov. are alphaproteobacterial root‐nodule bacteria that specifically nodulate and fix nitrogen with geographically and taxonomically separate legume hosts. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 62:2579–2588. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

