Pantoea sp. P37 as a novel nonpathogenic host for the heterologous production of rhamnolipids
- PMID: 32113194
- PMCID: PMC7221421
- DOI: 10.1002/mbo3.1019
Pantoea sp. P37 as a novel nonpathogenic host for the heterologous production of rhamnolipids
Abstract
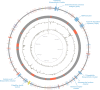
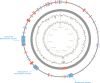
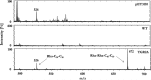
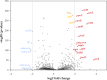
Microbially derived surfactants, so-called biosurfactants, have attracted significant attention as an environmentally friendly alternative to their chemically synthesized counterparts. Particularly, rhamnolipids offer a large potential with their outstanding surfactant properties such as complete biodegradability, low toxicity, and stability. Rhamnolipids are naturally synthesized by the opportunistic human pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa under the tight regulation of a highly complex quorum-sensing system. The heterologous production of mono-rhamnolipids by a newly isolated nonpathogenic strain of the genus Pantoea was investigated. Analysis of the genome obtained by a chimeric assembly of Nanopore long reads and high-quality Illumina reads suggested that the strain has evolved to an epiphytic rather than a pathogenic lifestyle. Functional heterologous expression of the mono-rhamnolipid operon rhlAB derived from a P. aeruginosa strain was established and confirmed by HPLC analysis. Transcriptome analysis indicated destabilizing effects of the produced rhamnolipids on the cell envelope of the host resulting in the induction of molecular stress responses. After integration of the rmlBCDA operon, extracellular rhamnolipids in amounts up to 0.4 g/L could be detected and were identified as a mono-rhamnolipid Rha-C10 -C10 by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry.
Keywords: Pantoea; biosurfactants; genome sequencing; heterologous expression; rhamnolipids.
© 2020 The Authors. MicrobiologyOpen published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures

References
-
- Abdel‐Mawgoud, A. M. , Hausmann, R. , Lépine, F. , Müller, M. M. , & Déziel, E. (2011). Rhamnolipids: Detection, analysis, biosynthesis, genetic regulation, and bioengineering of production In Soberón‐Chávez G. (Ed.), Biosurfactants (vol. 20, pp. 13–55). Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer; 10.1007/978-3-642-14490-5_2 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

