CZ CELLxGENE Discover: a single-cell data platform for scalable exploration, analysis and modeling of aggregated data
- PMID: 39607691
- PMCID: PMC11701654
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkae1142
CZ CELLxGENE Discover: a single-cell data platform for scalable exploration, analysis and modeling of aggregated data
Abstract
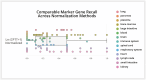
Hundreds of millions of single cells have been analyzed using high-throughput transcriptomic methods. The cumulative knowledge within these datasets provides an exciting opportunity for unlocking insights into health and disease at the level of single cells. Meta-analyses that span diverse datasets building on recent advances in large language models and other machine-learning approaches pose exciting new directions to model and extract insight from single-cell data. Despite the promise of these and emerging analytical tools for analyzing large amounts of data, the sheer number of datasets, data models and accessibility remains a challenge. Here, we present CZ CELLxGENE Discover (cellxgene.cziscience.com), a data platform that provides curated and interoperable single-cell data. Available via a free-to-use online data portal, CZ CELLxGENE hosts a growing corpus of community-contributed data of over 93 million unique cells. Curated, standardized and associated with consistent cell-level metadata, this collection of single-cell transcriptomic data is the largest of its kind and growing rapidly via community contributions. A suite of tools and features enables accessibility and reusability of the data via both computational and visual interfaces to allow researchers to explore individual datasets, perform cross-corpus analysis, and run meta-analyses of tens of millions of cells across studies and tissues at the resolution of single cells.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures





References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

