CO(2) uptake and fixation by a thermoacidophilic microbial community attached to precipitated sulfur in a geothermal spring
- PMID: 19429558
- PMCID: PMC2704841
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.02751-08
CO(2) uptake and fixation by a thermoacidophilic microbial community attached to precipitated sulfur in a geothermal spring
Abstract
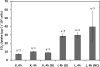
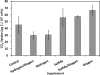
Carbon fixation at temperatures above 73 degrees C, the upper limit for photosynthesis, is carried out by chemosynthetic thermophiles. Yellowstone National Park (YNP), Wyoming possesses many thermal features that, while too hot for photosynthesis, presumably support chemosynthetic-based carbon fixation. To our knowledge, in situ rates of chemosynthetic reactions at these high temperatures in YNP or other high-temperature terrestrial geothermal springs have not yet been reported. A microbial community attached to precipitated elemental sulfur (S(o) floc) at the source of Dragon Spring (73 degrees C, pH 3.1) in Norris Geyser Basin, YNP, exhibited a maximum rate of CO(2) uptake of 21.3 +/- 11.9 microg of C 10(7) cells(-1) h(-1). When extrapolated over the estimated total quantity of S(o) floc at the spring's source, the S(o) floc-associated microbial community accounted for the uptake of 121 mg of C h(-1) at this site. On a per-cell basis, the rate was higher than that calculated for a photosynthetic mat microbial community dominated by Synechococcus spp. in alkaline springs at comparable temperatures. A portion of the carbon taken up as CO(2) by the S(o) floc-associated biomass was recovered in the cellular nucleic acid pool, demonstrating that uptake was coupled to fixation. The most abundant sequences in a 16S rRNA clone library of the S(o) floc-associated community were related to chemolithoautotrophic Hydrogenobaculum strains previously isolated from springs in the Norris Geyser Basin. These microorganisms likely contributed to the uptake and fixation of CO(2) in this geothermal habitat.
Figures

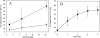
References
-
- Boyd, E. S., D. E. Cummings, and G. G. Geesey. 2007. Mineralogy influences structure and diversity of bacterial communities associated with geological substrata in a pristine aquifer. Microb. Ecol. 54:170-182. - PubMed
-
- Boyd, E. S., R. A. Jackson, G. Encarnacion, J. A. Zahn, T. Beard, W. D. Leavitt, Y. Pi, C. L. Zhang, A. Pearson, and G. G. Geesey. 2007. Isolation, characterization, and ecology of sulfur-respiring Crenarchaea inhabiting acid-sulfate-chloride geothermal springs in Yellowstone National Park. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 73:6669-6677. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brock, T. D. 1967. Life at high temperatures. Science 158:1012-1019. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

