Ancestral European roots of Helicobacter pylori in India
- PMID: 17584914
- PMCID: PMC1925095
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-8-184
Ancestral European roots of Helicobacter pylori in India
Abstract
Background: The human gastric pathogen Helicobacter pylori is co-evolved with its host and therefore, origins and expansion of multiple populations and sub populations of H. pylori mirror ancient human migrations. Ancestral origins of H. pylori in the vast Indian subcontinent are debatable. It is not clear how different waves of human migrations in South Asia shaped the population structure of H. pylori. We tried to address these issues through mapping genetic origins of present day H. pylori in India and their genomic comparison with hundreds of isolates from different geographic regions.
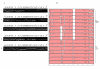
Results: We attempted to dissect genetic identity of strains by multilocus sequence typing (MLST) of the 7 housekeeping genes (atpA, efp, ureI, ppa, mutY, trpC, yphC) and phylogeographic analysis of haplotypes using MEGA and NETWORK software while incorporating DNA sequences and genotyping data of whole cag pathogenicity-islands (cagPAI). The distribution of cagPAI genes within these strains was analyzed by using PCR and the geographic type of cagA phosphorylation motif EPIYA was determined by gene sequencing. All the isolates analyzed revealed European ancestry and belonged to H. pylori sub-population, hpEurope. The cagPAI harbored by Indian strains revealed European features upon PCR based analysis and whole PAI sequencing.
Conclusion: These observations suggest that H. pylori strains in India share ancestral origins with their European counterparts. Further, non-existence of other sub-populations such as hpAfrica and hpEastAsia, at least in our collection of isolates, suggest that the hpEurope strains enjoyed a special fitness advantage in Indian stomachs to out-compete any endogenous strains. These results also might support hypotheses related to gene flow in India through Indo-Aryans and arrival of Neolithic practices and languages from the Fertile Crescent.
Figures



References
-
- Falush D, Wirth T, Linz B, Pritchard JK, Stephens M, Kidd M, Blaser MJ, Graham DY, Vacher S, Perez-Perez GI, Yamaoka Y, Mégraud F, Otto K, Reichard U, Katzowitsch E, Wang X, Achtman M, Suerbaum S. Traces of human migrations in Helicobacter pylori populations. Science. 2003;299:1582–1585. doi: 10.1126/science.1080857. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

