Height and Breast Cancer Risk: Evidence From Prospective Studies and Mendelian Randomization
- PMID: 26296642
- PMCID: PMC4643630
- DOI: 10.1093/jnci/djv219
Height and Breast Cancer Risk: Evidence From Prospective Studies and Mendelian Randomization
Abstract
Background: Epidemiological studies have linked adult height with breast cancer risk in women. However, the magnitude of the association, particularly by subtypes of breast cancer, has not been established. Furthermore, the mechanisms of the association remain unclear.
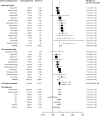
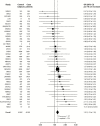
Methods: We performed a meta-analysis to investigate associations between height and breast cancer risk using data from 159 prospective cohorts totaling 5216302 women, including 113178 events. In a consortium with individual-level data from 46325 case patients and 42482 control patients, we conducted a Mendelian randomization analysis using a genetic score that comprised 168 height-associated variants as an instrument. This association was further evaluated in a second consortium using summary statistics data from 16003 case patients and 41335 control patients.
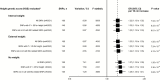
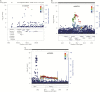
Results: The pooled relative risk of breast cancer was 1.17 (95% confidence interval [CI] = 1.15 to 1.19) per 10cm increase in height in the meta-analysis of prospective studies. In Mendelian randomization analysis, the odds ratio of breast cancer per 10cm increase in genetically predicted height was 1.22 (95% CI = 1.13 to 1.32) in the first consortium and 1.21 (95% CI = 1.05 to 1.39) in the second consortium. The association was found in both premenopausal and postmenopausal women but restricted to hormone receptor-positive breast cancer. Analyses of height-associated variants identified eight new loci associated with breast cancer risk after adjusting for multiple comparisons, including three loci at 1q21.2, DNAJC27, and CCDC91 at genome-wide significance level P < 5×10(-8).
Conclusions: Our study provides strong evidence that adult height is a risk factor for breast cancer in women and certain genetic factors and biological pathways affecting adult height have an important role in the etiology of breast cancer.
© The Author 2015. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61 (2):69–90. - PubMed
-
- Gunnell D, Okasha M, Smith GD, Oliver SE, Sandhu J, Holly JM. Height, leg length, and cancer risk: a systematic review. Epidemiol Rev. 2001;23 (2):313–342. - PubMed
-
- Okasha M, McCarron P, Gunnell D, Smith GD. Exposures in childhood, adolescence and early adulthood and breast cancer risk: a systematic review of the literature. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2003;78 (2):223–276. - PubMed
-
- Friedenreich CM. Review of anthropometric factors and breast cancer risk. Eur J Cancer Prev. 2001;10 (1):15–32. - PubMed
-
- Tornberg SA, Holm LE, Carstensen JM. Breast cancer risk in relation to serum cholesterol, serum beta-lipoprotein, height, weight, and blood pressure. Acta Oncol. 1988;27 (1):31–37. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- CA54281/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA176785/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA016056/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 CA164920/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA015704/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CAPMC/ CIHR/Canada
- C12292/A11174/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- 16459/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- R01 CA128978/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA116201/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA063464/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- C5047/A15007/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- C1281/A12014/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- CA098758/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 CA182910/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA128978/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 CA197449/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 CA070867/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 16565/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- RG/08/014/24067/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- 1U19 CA148065/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- C5047/A10692/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- U01 CA164930/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 1U19 CA148537/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- MR/L003120/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- CA63464/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- C490/A10124/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- U01 CA116167/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- C5047/A8384/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- C1287/A 10710/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- CA116167/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA176785/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA116167/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 16563/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- U01 CA063464/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA077398/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA054281/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA132839/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA164920/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 1U19 CA148112/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37CA070867/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA098758/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA132839/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U19 CA148065/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 10119/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- C1287/A10118/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- U01 CA164973/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 CA054281/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 16561/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- 10124/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

