Problem-based learning for in-service training on breastfeeding in Friuli Venezia Giulia, Italy
- PMID: 34838079
- PMCID: PMC8626965
- DOI: 10.1186/s13006-021-00439-4
Problem-based learning for in-service training on breastfeeding in Friuli Venezia Giulia, Italy
Abstract
Background: Problem-Based Learning (PBL) is extensively used in pre- and post-graduate teaching programmes. However, it has been seldom used for in-service training and continuing medical education. We aimed to develop a PBL curriculum for a short in-service training on breastfeeding for maternal and child health professionals, and to assess the effect of these courses on their knowledge and skills. Also, the project aimed at increasing exclusive breastfeeding rates and duration in an Italian region.
Methods: After initial training on PBL and an assessment of the learning needs of about 400 health professionals, a small working group developed learning objectives, designed a curriculum, produced manuals, and shaped assessment tools for a new PBL course on breastfeeding. The field test of the new course allowed selection of the tutors for the scaling up of the training to the whole region. During this extension phase, participants were asked to complete an evaluation questionnaire. In addition, the health professionals who attended the PBL courses in 2019 were asked to complete an online survey to assess knowledge, attitudes and practices (KAP) just before, soon after the course, and 4-6 months later.
Results: The new 29 - hour PBL course, to be delivered in four days over four consecutive weeks, gives priority to tutorial groups and practical activities (71% of the total time). Supervised clinical practices absorb 16% of time. Ethics, communication and woman-centred clinical management content run throughout the four days and all activities. The three manuals, for tutors, participants and practical activities, facilitate the tasks and performance of tutors and participants. After the field test, 32 regional tutors ran courses for 562 health professionals. The analysis of the evaluation showed a high level of satisfaction for perceived effectiveness, relevance to practice, and educational quality. The KAP questionnaires indicated a general improvement after the course and retention after 4-6 months.
Conclusions: Despite some predictable shortcomings, this new PBL approach for short in-service training courses on breastfeeding showed encouraging results as far as participants' satisfaction and KAP are concerned. The possible effects on rates and duration of exclusive breastfeeding need further research.
Keywords: Breastfeeding; Continuing medical education; In-service training; Italy; Problem based curriculum; Problem-based learning.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
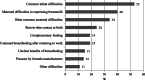
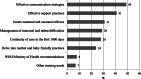

References
-
- Ministero della Salute . Linee di indirizzo nazionali sulla protezione, la promozione ed il sostegno dell’allattamento al seno [National policy for the protection, promotion and support of breastfeeding] Rome: Gazzetta Ufficiale; 2008.
-
- ISTAT . Gravidanza, parto e allattamento in 2013 [pregnancy, birth and breastfeeding in 2013] Rome: ISTAT; 2014.
-
- UNICEF Italy. Insieme per l’allattamento [Together for breastfeeding]. https://www.unicef.it/italia-amica-dei-bambini/insieme-per-allattamento/ accessed September 1, 2021.
-
- WHO . Breastfeeding counselling: a training course. Geneva: WHO; 1993.
-
- UNICEF . Breastfeeding, management and promotion in a baby friendly hospital: an 18hour course for maternity staff. New York: UNICEF; 1993.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

