Herbivory rapidly activates MAPK signaling in attacked and unattacked leaf regions but not between leaves of Nicotiana attenuata
- PMID: 17400894
- PMCID: PMC1867352
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.106.049353
Herbivory rapidly activates MAPK signaling in attacked and unattacked leaf regions but not between leaves of Nicotiana attenuata
Abstract
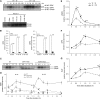
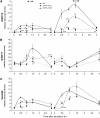
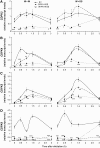
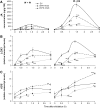
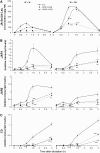
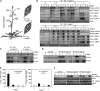
Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling plays a central role in transducing extracellular stimuli into intracellular responses, but its role in mediating plant responses to herbivore attack remains largely unexplored. When Manduca sexta larvae attack their host plant, Nicotiana attenuata, the plant's wound response is reconfigured at transcriptional, phytohormonal, and defensive levels due to the introduction of oral secretions (OS) into wounds during feeding. We show that OS dramatically amplify wound-induced MAPK activity and that fatty acid-amino acid conjugates in M. sexta OS are the elicitors. Virus-induced gene silencing of salicylic acid-induced protein kinase (SIPK) and wound-induced protein kinase revealed their importance in mediating wound and OS-elicited hormonal responses and transcriptional regulation of defense-related genes. We found that after applying OS to wounds created in one portion of a leaf, SIPK is activated in both wounded and specific unwounded regions of the leaf but not in phylotactically connected adjacent leaves. We propose that M. sexta attack elicits a mobile signal that travels to nonwounded regions of the attacked leaf where it activates MAPK signaling and, thus, downstream responses; subsequently, a different signal is transported by the vascular system to systemic leaves to initiate defense responses without activating MAPKs in systemic leaves.
Figures







References
-
- Ahlfors, R., Macioszek, V., Rudd, J., Brosche, M., Schlichting, R., Scheel, D., and Kangasjarvi, J. (2004). Stress hormone-independent activation and nuclear translocation of mitogen-activated protein kinases in Arabidopsis thaliana during ozone exposure. Plant J. 40 512–522. - PubMed
-
- Alarcon, J.J., and Malone, M. (1994). Substantial hydraulic signals are triggered by leaf-biting insects in tomato. J. Exp. Bot. 45 953–957.
-
- Alborn, H.T., Brennan, M.M., and Tumlinson, J.H. (2003). Differential activity and degradation of plant volatile elicitors in regurgitant of tobacco hornworm (Manduca sexta) larvae. J. Chem. Ecol. 29 1357–1372. - PubMed
-
- Alborn, T., Turlings, T.C.J., Jones, T.H., Stenhagen, G., Loughrin, J.H., and Tumlinson, J.H. (1997). An elicitor of plant volatiles from beet armyworm oral secretion. Science 276 945–949.
-
- Allwood, E.G., Davies, D.R., Gerrish, C., Ellis, B.E., and Bolwell, G.P. (1999). Phosphorylation of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase: Evidence for a novel protein kinase and identification of the phosphorylated residue. FEBS Lett. 457 47–52. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

