Superoxide dismutase from the eukaryotic thermophile Alvinella pompejana: structures, stability, mechanism, and insights into amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- PMID: 19063897
- PMCID: PMC2669833
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2008.11.031
Superoxide dismutase from the eukaryotic thermophile Alvinella pompejana: structures, stability, mechanism, and insights into amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
Abstract
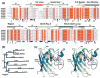
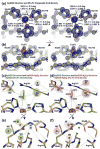
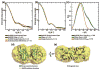
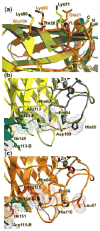
Prokaryotic thermophiles supply stable human protein homologs for structural biology; yet, eukaryotic thermophiles would provide more similar macromolecules plus those missing in microbes. Alvinella pompejana is a deep-sea hydrothermal-vent worm that has been found in temperatures averaging as high as 68 degrees C, with spikes up to 84 degrees C. Here, we used Cu,Zn superoxide dismutase (SOD) to test if this eukaryotic thermophile can provide insights into macromolecular mechanisms and stability by supplying better stable mammalian homologs for structural biology and other biophysical characterizations than those from prokaryotic thermophiles. Identification, cloning, characterization, X-ray scattering (small-angle X-ray scattering, SAXS), and crystal structure determinations show that A. pompejana SOD (ApSOD) is superstable, homologous, and informative. SAXS solution analyses identify the human-like ApSOD dimer. The crystal structure shows the active site at 0.99 A resolution plus anchoring interaction motifs in loops and termini accounting for enhanced stability of ApSOD versus human SOD. Such stabilizing features may reduce movements that promote inappropriate intermolecular interactions, such as amyloid-like filaments found in SOD mutants causing the neurodegenerative disease familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis or Lou Gehrig's disease. ApSOD further provides the structure of a long-sought SOD product complex at 1.35 A resolution, suggesting a unified inner-sphere mechanism for catalysis involving metal ion movement. Notably, this proposed mechanism resolves apparent paradoxes regarding electron transfer. These results extend knowledge of SOD stability and catalysis and suggest that the eukaryote A. pompejana provides macromolecules highly similar to those from humans, but with enhanced stability more suitable for scientific and medical applications.
Figures


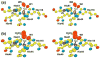

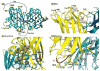
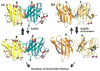
References
-
- Egorova K, Antranikian G. Industrial relevance of thermophilic Archaea. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2005;8:649–55. - PubMed
-
- Yano JK, Poulos TL. New understandings of thermostable and peizostable enzymes. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2003;14:360–5. - PubMed
-
- Fan L, Williams RS, Shin DS, Chapados BR, Tainer JA. Master keys to DNA replication, repair, and recombination from the structural biology of enzymes from thermophiles. In: Robb FT, Antranikian G, Grogan D, Driessen A, editors. Thermophiles: biology and technology at high temperatures. CRC Press; Boca Raton, FL: 2008. pp. 239–263.
-
- DiDonato M, Deacon AM, Klock HE, McMullan D, Lesley SA. A scaleable and integrated crystallization pipeline applied to mining the Thermotoga maritima proteome. J Struct Funct Genomics. 2004;5:133–46. - PubMed
-
- Robinson-Rechavi M, Alibes A, Godzik A. Contribution of electrostatic interactions, compactness and quaternary structure to protein thermostability: lessons from structural genomics of Thermotoga maritima. J Mol Biol. 2006;356:547–57. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

