Assembly of the cnidarian camera-type eye from vertebrate-like components
- PMID: 18577593
- PMCID: PMC2449352
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0800388105
Assembly of the cnidarian camera-type eye from vertebrate-like components
Abstract
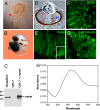
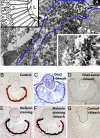
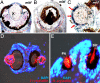
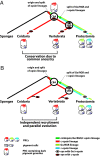
Animal eyes are morphologically diverse. Their assembly, however, always relies on the same basic principle, i.e., photoreceptors located in the vicinity of dark shielding pigment. Cnidaria as the likely sister group to the Bilateria are the earliest branching phylum with a well developed visual system. Here, we show that camera-type eyes of the cubozoan jellyfish, Tripedalia cystophora, use genetic building blocks typical of vertebrate eyes, namely, a ciliary phototransduction cascade and melanogenic pathway. Our findings indicative of parallelism provide an insight into eye evolution. Combined, the available data favor the possibility that vertebrate and cubozoan eyes arose by independent recruitment of orthologous genes during evolution.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Fernald RD. Casting a genetic light on the evolution of eyes. Science. 2006;313:1914–1918. - PubMed
-
- Arendt D. Evolution of eyes and photoreceptor cell types. Int J Dev Biol. 2003;47:563–571. - PubMed
-
- Viscontini M, Hummel W, Fischer A. Isolation of pterin dimers from the eyes of Platynereis dumerilii (German) Helv Chim Acta. 1970;53:1207–1209.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

