Characterization of ESBL (SHV-12) producing clinical isolate of Enterobacter aerogenes from a tertiary care hospital in Nigeria
- PMID: 20067633
- PMCID: PMC2817643
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-0711-9-1
Characterization of ESBL (SHV-12) producing clinical isolate of Enterobacter aerogenes from a tertiary care hospital in Nigeria
Abstract
Background: We studied the beta-lactamases of an E. aerogenes isolate recovered from the blood of a two-year-old patient. The isolate demonstrated a disk-diffusion phenotype typical for an AmpC-ESBL co-producer.
Methods: Microbiology studies were performed according to standard protocols. The resistance gene was identified by transconjugation and cloning experiments.
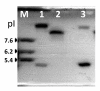
Results: By transconjugation only a narrow spectrum beta-lactamase (TEM-1) encoded on a small plasmid was transmitted. The ESBL was cloned and expressed in an E. coli host. Sequence analysis of the recombinant plasmid revealed blaSHV-12 associated to the insertion sequence, IS26.
Conclusion: This is the first study demonstrated the occurrence of SHV-12 in Nigeria.
Figures

References
-
- Chow JW, Fine MJ, Shlaes DM, Quinn JP, Hooper DC, Johnson MP, Ramphal R, Wagener MM, Miyashiro DK, Yu VL. Enterobacter bacteremia: clinical features and emergence of antibiotic resistance during therapy. Annals of internal medicine. 1991;115:585–590. - PubMed
-
- Pfaller MA, Jones RN, Marshall SA, Coffman SL, Hollis RJ, Edmond MB, Wenzel RP. Inducible amp C beta-lactamase producing gram-negative bacilli from blood stream infections: frequency, antimicrobial susceptibility, and molecular epidemiology in a national surveillance program (SCOPE) Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1997;28:211–219. doi: 10.1016/S0732-8893(97)00064-3. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

