Polarization of the C. elegans embryo by RhoGAP-mediated exclusion of PAR-6 from cell contacts
- PMID: 18583611
- PMCID: PMC2670547
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1156063
Polarization of the C. elegans embryo by RhoGAP-mediated exclusion of PAR-6 from cell contacts
Abstract
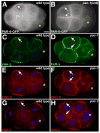
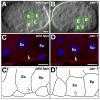
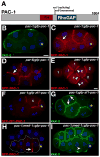
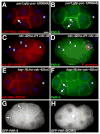
Early embryos of some metazoans polarize radially to facilitate critical patterning events such as gastrulation and asymmetric cell division; however, little is known about how radial polarity is established. Early embryos of Caenorhabditis elegans polarize radially when cell contacts restrict the polarity protein PAR-6 to contact-free cell surfaces, where PAR-6 regulates gastrulation movements. We have identified a Rho guanosine triphosphatase activating protein (RhoGAP), PAC-1, which mediates C. elegans radial polarity and gastrulation by excluding PAR-6 from contacted cell surfaces. We show that PAC-1 is recruited to cell contacts, and we suggest that PAC-1 controls radial polarity by restricting active CDC-42 to contact-free surfaces, where CDC-42 binds and recruits PAR-6. Thus, PAC-1 provides a dynamic molecular link between cell contacts and PAR proteins that polarizes embryos radially.
Figures
References
-
- Johnson MH, McConnell JM. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2004;15:583. - PubMed
-
- Nance J, Munro EM, Priess JR. Development. 2003;130:5339. - PubMed
-
- Lee JY, Goldstein B. Development. 2003;130:307. - PubMed
-
- Etemad-Moghadam B, Guo S, Kemphues KJ. Cell. 1995;83:743. - PubMed
-
- Hung TJ, Kemphues KJ. Development. 1999;126:127. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

