Identification of clinically relevant nonhemolytic Streptococci on the basis of sequence analysis of 16S-23S intergenic spacer region and partial gdh gene
- PMID: 19193846
- PMCID: PMC2668326
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.01449-08
Identification of clinically relevant nonhemolytic Streptococci on the basis of sequence analysis of 16S-23S intergenic spacer region and partial gdh gene
Abstract
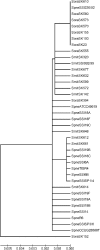
Nonhemolytic streptococci (NHS) cause serious infections, such as endocarditis and septicemia. Many conventional phenotypic methods are insufficient for the identification of bacteria in this group to the species level. Genetic analysis has revealed that single-gene analysis is insufficient for the identification of all species in this group of bacteria. The aim of the present study was to establish a method based on sequence analysis of the 16S-23S intergenic spacer (ITS) region and the partial gdh gene to identify clinical relevant NHS to the species level. Sequence analysis of the ITS region was performed with 57 NHS reference or clinical strains. Satisfactory identification to the species level was achieved for 14/19 NHS species included in this study on the basis of sequence analysis of the ITS region. Streptococcus salivarius and Streptococcus vestibularis obtained the expected taxon as the best taxon match, but there was a short maximum score distance to the next best match (distance, <10). Streptococcus mitis, Streptococcus oralis, and Streptococcus pneumoniae could not be unambiguously discriminated by sequence analysis of the ITS region, as was also proven by phylogenetic analysis. These five species could be identified to the group level only by ITS sequence analysis. Partial gdh sequence analysis was applied to the 11 S. oralis strains, the 11 S. mitis strains, and the 17 S. pneumoniae strains. All except one strain achieved a satisfactory identification to the species level. A phylogenetic algorithm based on the analysis of partial gdh gene sequences revealed three distinct clusters. We suggest that sequence analysis of the combination of the ITS region and the partial gdh gene can be used in the reference laboratory for the species-level identification of NHS.
Figures

References
-
- Arbique, J. C., C. Poyart, P. Trieu-Cuot, G. Quesne, M. G. Carvalho, A. G. Steigerwalt, R. E. Morey, D. Jackson, R. J. Davidson, and R. R. Facklam. 2004. Accuracy of phenotypic and genotypic testing for identification of Streptococcus pneumoniae and description of Streptococcus pseudopneumoniae sp. nov. J. Clin. Microbiol. 424686-4696. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bek-Thomsen, M., H. Tettelin, I. Hance, K. E. Nelson, and M. Kilian. 2008. Population diversity and dynamics of Streptococcus mitis, Streptococcus oralis, and Streptococcus infantis in the upper respiratory tracts of adults, determined by a nonculture strategy. Infect. Immun. 761889-1896. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Carley, N. H. 1992. Streptococcus salivarius bacteremia and meningitis following upper gastrointestinal endoscopy and cauterization for gastric bleeding. Clin. Infect. Dis. 14947-948. - PubMed
-
- Carratala, J., B. Roson, A. Fernandez-Sevilla, F. Alcaide, and F. Gudiol. 1998. Bacteremic pneumonia in neutropenic patients with cancer: causes, empirical antibiotic therapy, and outcome. Arch. Intern. Med. 158868-872. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

