A recurrent 15q13.3 microdeletion syndrome associated with mental retardation and seizures
- PMID: 18278044
- PMCID: PMC2365467
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.93
A recurrent 15q13.3 microdeletion syndrome associated with mental retardation and seizures
Abstract
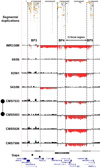
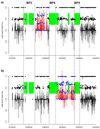
We report a recurrent microdeletion syndrome causing mental retardation, epilepsy and variable facial and digital dysmorphisms. We describe nine affected individuals, including six probands: two with de novo deletions, two who inherited the deletion from an affected parent and two with unknown inheritance. The proximal breakpoint of the largest deletion is contiguous with breakpoint 3 (BP3) of the Prader-Willi and Angelman syndrome region, extending 3.95 Mb distally to BP5. A smaller 1.5-Mb deletion has a proximal breakpoint within the larger deletion (BP4) and shares the same distal BP5. This recurrent 1.5-Mb deletion contains six genes, including a candidate gene for epilepsy (CHRNA7) that is probably responsible for the observed seizure phenotype. The BP4-BP5 region undergoes frequent inversion, suggesting a possible link between this inversion polymorphism and recurrent deletion. The frequency of these microdeletions in mental retardation cases is approximately 0.3% (6/2,082 tested), a prevalence comparable to that of Williams, Angelman and Prader-Willi syndromes.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Stankiewicz P, Lupski JR. Genome architecture, rearrangements and genomic disorders. Trends Genet. 2002;18:74–82. - PubMed
-
- Sharp AJ, Hansen S, Selzer RR, Cheng Z, Regan R, Hurst JA, Stewart H, Price SM, Blair E, Hennekam RC, et al. Discovery of previously unidentified genomic disorders from the duplication architecture of the human genome. Nat Genet. 2006;38:1038–1042. - PubMed
-
- Jiang Z, Tang H, Ventura M, Cardone MF, Marques-Bonet T, She X, Pevzner PA, Eichler EE. Ancestral reconstruction of segmental duplications reveals punctuated cores of human genome evolution. Nat Genet. 2007;39:1361–1368. - PubMed
-
- Zody MC, Garber M, Sharpe T, Young SK, Rowen L, O'Neill K, Whittaker CA, Kamal M, Chang JL, Cuomo CA, et al. Analysis of the DNA sequence and duplication history of human chromosome 15. Nature. 2006;440:671–675. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

