A LAMP sequencing approach for high-throughput co-detection of SARS-CoV-2 and influenza virus in human saliva
- PMID: 35532013
- PMCID: PMC9084890
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.69949
A LAMP sequencing approach for high-throughput co-detection of SARS-CoV-2 and influenza virus in human saliva
Abstract
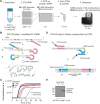
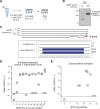
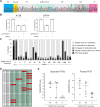
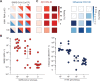
The COVID-19 pandemic has created an urgent need for rapid, effective, and low-cost SARS-CoV-2 diagnostic testing. Here, we describe COV-ID, an approach that combines RT-LAMP with deep sequencing to detect SARS-CoV-2 in unprocessed human saliva with a low limit of detection (5-10 virions). Based on a multi-dimensional barcoding strategy, COV-ID can be used to test thousands of samples overnight in a single sequencing run with limited labor and laboratory equipment. The sequencing-based readout allows COV-ID to detect multiple amplicons simultaneously, including key controls such as host transcripts and artificial spike-ins, as well as multiple pathogens. Here, we demonstrate this flexibility by simultaneous detection of 4 amplicons in contrived saliva samples: SARS-CoV-2, influenza A, human STATHERIN, and an artificial SARS calibration standard. The approach was validated on clinical saliva samples, where it showed excellent agreement with RT-qPCR. COV-ID can also be performed directly on saliva absorbed on filter paper, simplifying collection logistics and sample handling.
Keywords: COVID; RT-LAMP; human; infectious disease; microbiology; sequencing; testing; viruses.
© 2022, Warneford-Thomson et al.
Conflict of interest statement
RW, PS, PL, JL, JM, AD, KZ, JS, RJ, CT No competing interests declared, BA Research funding from Becton Dickinson Speaking honoraria from Becton Dickinson, Stryker Equity in VOC Health, a company developing novel COVID19 detection technology distinct from the topic of this manuscript, RB Reviewing editor, eLife
Figures




References
-
- Augustine R, Hasan A, Das S, Ahmed R, Mori Y, Notomi T, Kevadiya BD, Thakor AS. Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP): A Rapid, Sensitive, Specific, and Cost-Effective Point-of-Care Test for Coronaviruses in the Context of COVID-19 Pandemic. Biology. 2020;9:E182. doi: 10.3390/biology9080182. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aynaud M-M, Hernandez JJ, Barutcu S, Braunschweig U, Chan K, Pearson JD, Trcka D, Prosser SL, Kim J, Barrios-Rodiles M, Jen M, Song S, Shen J, Bruce C, Hazlett B, Poutanen S, Attisano L, Bremner R, Blencowe BJ, Mazzulli T, Han H, Pelletier L, Wrana JL. A multiplexed, next generation sequencing platform for high-throughput detection of SARS-CoV-2. Nature Communications. 2021;12:1405. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-21653-y. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bloom JS, Sathe L, Munugala C, Jones EM, Gasperini M, Lubock NB, Yarza F, Thompson EM, Kovary KM, Park J, Marquette D, Kay S, Lucas M, Love T, Sina Booeshaghi A, Brandenberg OF, Guo L, Boocock J, Hochman M, Simpkins SW, Lin I, LaPierre N, Hong D, Zhang Y, Oland G, Choe BJ, Chandrasekaran S, Hilt EE, Butte MJ, Damoiseaux R, Kravit C, Cooper AR, Yin Y, Pachter L, Garner OB, Flint J, Eskin E, Luo C, Kosuri S, Kruglyak L, Arboleda VA. Massively scaled-up testing for SARS-CoV-2 RNA via next-generation sequencing of pooled and barcoded nasal and saliva samples. Nature Biomedical Engineering. 2021;5:657–665. doi: 10.1038/s41551-021-00754-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

