Reprogramming of the microRNA transcriptome mediates resistance to rapamycin
- PMID: 23300087
- PMCID: PMC3585042
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.416446
Reprogramming of the microRNA transcriptome mediates resistance to rapamycin
Abstract
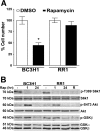
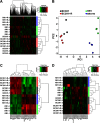
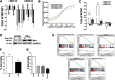
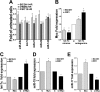
The mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) is a central regulator of cell proliferation that is often deregulated in cancer. Inhibitors of mTOR, including rapamycin and its analogues, are being evaluated as antitumor agents. For their promise to be fulfilled, it is of paramount importance to identify the mechanisms of resistance and develop novel therapies to overcome it. Given the emerging role of microRNAs (miRNAs) in tumorigenesis, we hypothesized that miRNAs could play important roles in the response of tumors to mTOR inhibitors. Long-term rapamycin treatment showed extensive reprogramming of miRNA expression, characterized by up-regulation of miR-17-92 and related clusters and down-regulation of tumor suppressor miRNAs. Inhibition of members of the miR-17-92 clusters or delivery of tumor suppressor miRNAs restored sensitivity to rapamycin. This study identifies miRNAs as new downstream components of the mTOR-signaling pathway, which may determine the response of tumors to mTOR inhibitors. It also identifies potential markers to assess the efficacy of treatment and provides novel therapeutic targets to treat rapamycin-resistant tumors.
Figures

References
-
- Kim D. H., Sarbassov D. D., Ali S. M., King J. E., Latek R. R., Erdjument-Bromage H., Tempst P., Sabatini D. M. (2002) mTOR interacts with raptor to form a nutrient-sensitive complex that signals to the cell growth machinery. Cell 110, 163–175 - PubMed
-
- Sarbassov D. D., Ali S. M., Kim D. H., Guertin D. A., Latek R. R., Erdjument-Bromage H., Tempst P., Sabatini D. M. (2004) Rictor, a novel binding partner of mTOR, defines a rapamycin-insensitive and raptor-independent pathway that regulates the cytoskeleton. Curr. Biol. 14, 1296–1302 - PubMed
-
- Sabatini D. M. (2006) mTOR and cancer: insights into a complex relationship. Nat. Rev. Cancer 6, 729–734 - PubMed
-
- Sarbassov D. D., Ali S. M., Sabatini D. M. (2005) Growing roles for the mTOR pathway. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 17, 596–603 - PubMed
-
- Sarbassov D. D., Guertin D. A., Ali S. M., Sabatini D. M. (2005) Phosphorylation and regulation of Akt/PKB by the rictor-mTOR complex. Science 307, 1098–1101 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

