A Myc network accounts for similarities between embryonic stem and cancer cell transcription programs
- PMID: 20946988
- PMCID: PMC3018841
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.09.010
A Myc network accounts for similarities between embryonic stem and cancer cell transcription programs
Abstract
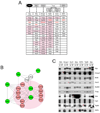
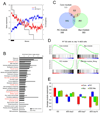
c-Myc (Myc) is an important transcriptional regulator in embryonic stem (ES) cells, somatic cell reprogramming, and cancer. Here, we identify a Myc-centered regulatory network in ES cells by combining protein-protein and protein-DNA interaction studies and show that Myc interacts with the NuA4 complex, a regulator of ES cell identity. In combination with regulatory network information, we define three ES cell modules (Core, Polycomb, and Myc) and show that the modules are functionally separable, illustrating that the overall ES cell transcription program is composed of distinct units. With these modules as an analytical tool, we have reassessed the hypothesis linking an ES cell signature with cancer or cancer stem cells. We find that the Myc module, independent of the Core module, is active in various cancers and predicts cancer outcome. The apparent similarity of cancer and ES cell signatures reflects, in large part, the pervasive nature of Myc regulatory networks.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




Comment in
-
The Myc connection: ES cells and cancer.Cell. 2010 Oct 15;143(2):184-6. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.09.046. Cell. 2010. PMID: 20946977
-
MYC matters.Nat Rev Cancer. 2010 Dec;10(12):812. doi: 10.1038/nrc2970. Nat Rev Cancer. 2010. PMID: 21155177 No abstract available.
References
-
- Bild AH, Yao G, Chang JT, Wang Q, Potti A, Chasse D, Joshi MB, Harpole D, Lancaster JM, Berchuck A, et al. Oncogenic pathway signatures in human cancers as a guide to targeted therapies. Nature. 2006;439:353–357. - PubMed
-
- Boyer LA, Plath K, Zeitlinger J, Brambrink T, Medeiros LA, Lee TI, Levine SS, Wernig M, Tajonar A, Ray MK, et al. Polycomb complexes repress developmental regulators in murine embryonic stem cells. Nature. 2006;441:349–353. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

