ChromatinHD connects single-cell DNA accessibility and conformation to gene expression through scale-adaptive machine learning
- PMID: 39747019
- PMCID: PMC11697365
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-55447-9
ChromatinHD connects single-cell DNA accessibility and conformation to gene expression through scale-adaptive machine learning
Abstract
Gene regulation is inherently multiscale, but scale-adaptive machine learning methods that fully exploit this property in single-nucleus accessibility data are still lacking. Here, we develop ChromatinHD, a pair of scale-adaptive models that uses the raw accessibility data, without peak-calling or windows, to link regions to gene expression and determine differentially accessible chromatin. We show how ChromatinHD consistently outperforms existing peak and window-based approaches and find that this is due to a large number of uniquely captured, functional accessibility changes within and outside of putative cis-regulatory regions. Furthermore, ChromatinHD can delineate collaborating regulatory regions, including their preferential genomic conformations, that drive gene expression. Finally, our models also use changes in ATAC-seq fragment lengths to identify dense binding of transcription factors, a feature not captured by footprinting methods. Altogether, ChromatinHD, available at https://chromatinhd.org , is a suite of computational tools that enables a data-driven understanding of chromatin accessibility at various scales and how it relates to gene expression.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

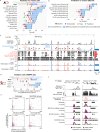


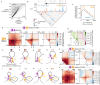
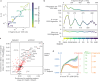
References
-
- Wu, C., Wong, Y. C. & Elgin, S. C. The chromatin structure of specific genes: II. Disruption of chromatin structure during gene activity. Cell16, 807–814 (1979). - PubMed
-
- Levy, A. & Noll, M. Chromatin fine structure of active and repressed genes. Nature289, 198–203 (1981). - PubMed
-
- Tedesco, M. et al. Chromatin Velocity reveals epigenetic dynamics by single-cell profiling of heterochromatin and euchromatin. Nat. Biotechnol.40, 235–244 (2022). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

