Direct reprogramming of fibroblasts into functional cardiomyocytes by defined factors
- PMID: 20691899
- PMCID: PMC2919844
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.07.002
Direct reprogramming of fibroblasts into functional cardiomyocytes by defined factors
Abstract
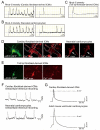
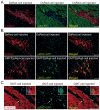
The reprogramming of fibroblasts to induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) raises the possibility that a somatic cell could be reprogrammed to an alternative differentiated fate without first becoming a stem/progenitor cell. A large pool of fibroblasts exists in the postnatal heart, yet no single "master regulator" of direct cardiac reprogramming has been identified. Here, we report that a combination of three developmental transcription factors (i.e., Gata4, Mef2c, and Tbx5) rapidly and efficiently reprogrammed postnatal cardiac or dermal fibroblasts directly into differentiated cardiomyocyte-like cells. Induced cardiomyocytes expressed cardiac-specific markers, had a global gene expression profile similar to cardiomyocytes, and contracted spontaneously. Fibroblasts transplanted into mouse hearts one day after transduction of the three factors also differentiated into cardiomyocyte-like cells. We believe these findings demonstrate that functional cardiomyocytes can be directly reprogrammed from differentiated somatic cells by defined factors. Reprogramming of endogenous or explanted fibroblasts might provide a source of cardiomyocytes for regenerative approaches.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
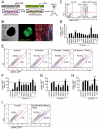
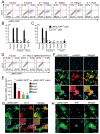
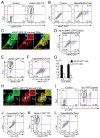
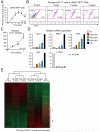

Comment in
- Regen Med. 2011 Jan;6(1):31-4
-
Getting to the heart of the matter: direct reprogramming to cardiomyocytes.Cell Stem Cell. 2010 Aug 6;7(2):139-41. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2010.07.004. Cell Stem Cell. 2010. PMID: 20682439
References
-
- Andersen DC, Andersen P, Schneider M, Jensen HB, Sheikh SP. Murine “cardiospheres” are not a source of stem cells with cardiomyogenic potential. Stem Cells. 2009;27:1571–1581. - PubMed
-
- Baeyens L, De Breuck S, Lardon J, Mfopou JK, Rooman I, Bouwens L. In vitro generation of insulin-producing beta cells from adult exocrine pancreatic cells. Diabetologia. 2005;48:49–57. - PubMed
-
- Baudino TA, Carver W, Giles W, Borg TK. Cardiac fibroblasts: friend or foe? Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2006;291:H1015–1026. - PubMed
-
- Beltrami AP, Barlucchi L, Torella D, Baker M, Limana F, Chimenti S, Kasahara H, Rota M, Musso E, Urbanek K, et al. Adult cardiac stem cells are multipotent and support myocardial regeneration. Cell. 2003;114:763–776. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein BE, Mikkelsen TS, Xie X, Kamal M, Huebert DJ, Cuff J, Fry B, Meissner A, Wernig M, Plath K, et al. A bivalent chromatin structure marks key developmental genes in embryonic stem cells. Cell. 2006;125:315–326. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

